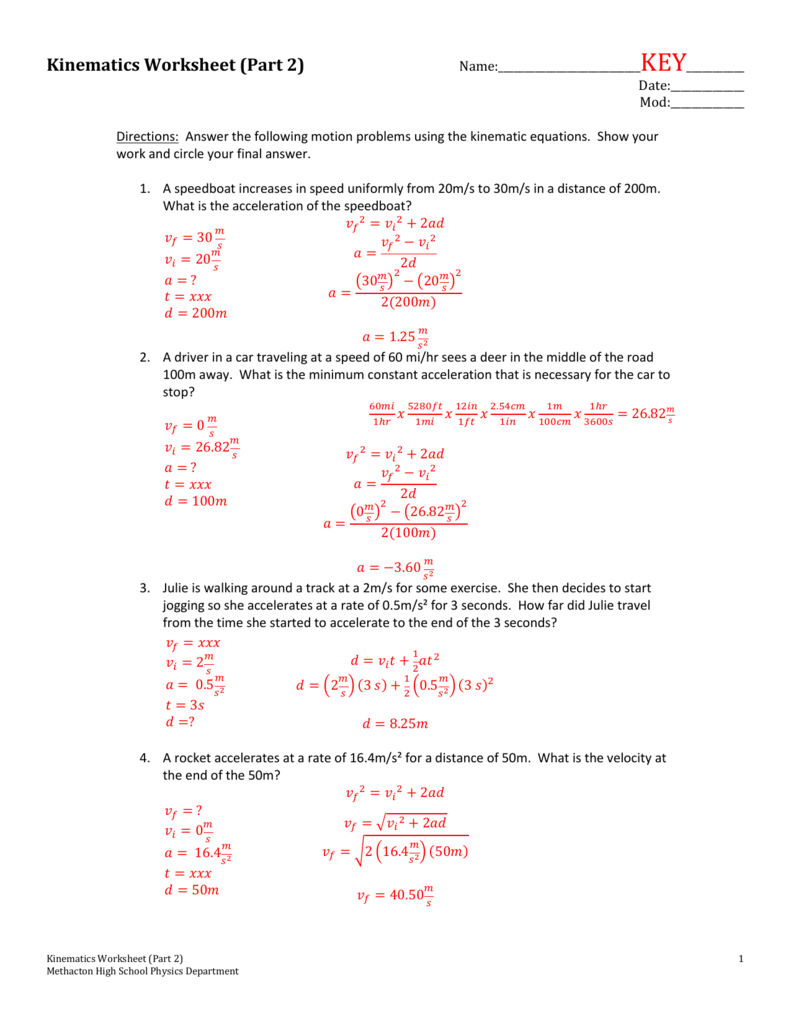
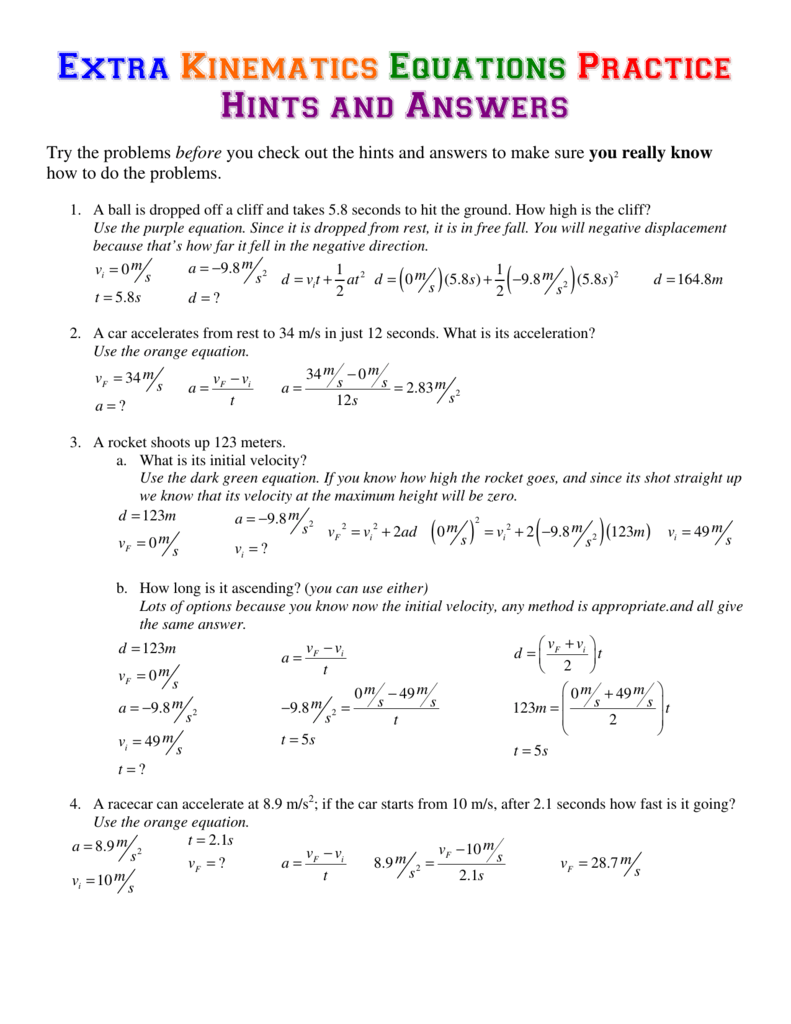
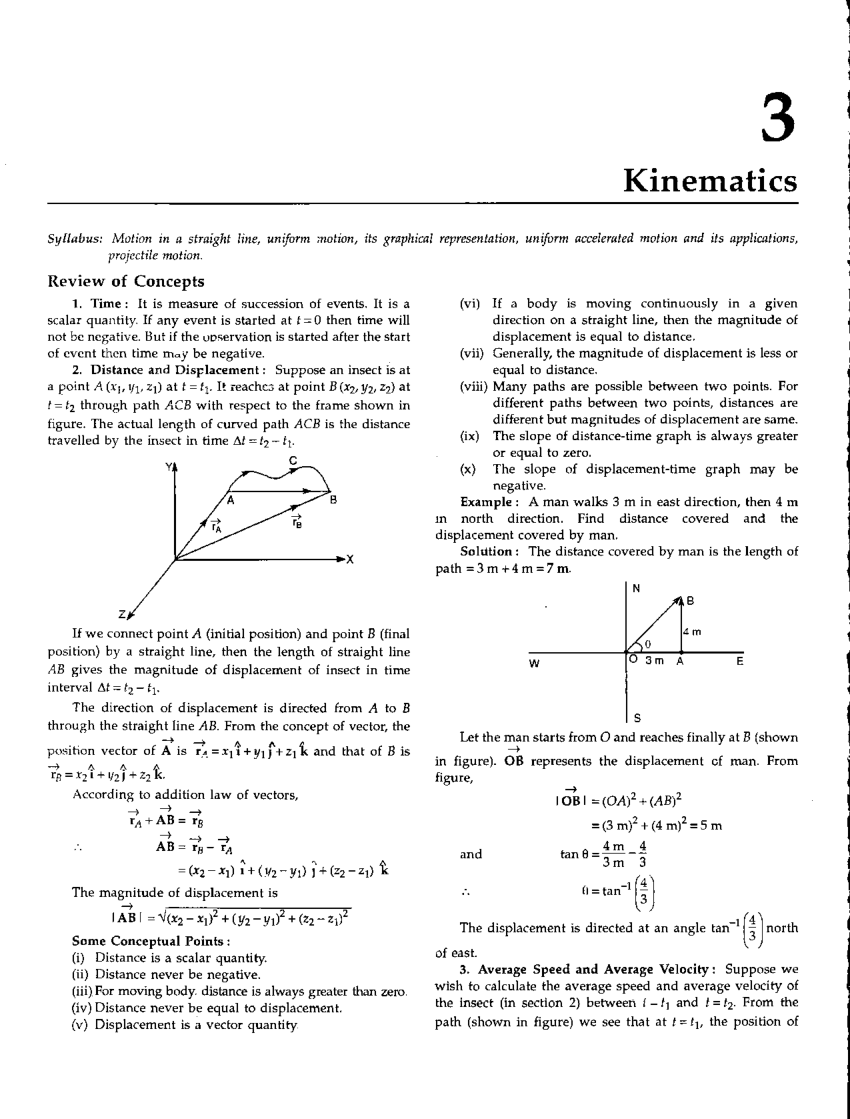
1-D Kinematics Acceleration Worksheet Answers
1-D Kinematics Acceleration Worksheet Answers - Particle moves from a point p to a point q in a time t. Web the solutions guide includes all the pdfs and source documents (ms word files) of the think sheets at the curriculum corner, along with answers, explanations, and solutions,. A race car can reach a velocity of 75.0 m/s in 3.72s. This is a simple 1d kinematics acceleration example. Web kinematic equations solve the following. Web up to 24% cash back time taken (1) 2. Determine the distance traveled before takeoff. A person can move very fast and thus have a large speed but if. Answer the following based on the velocity vs. How far would the same car travel when. Web web kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. How far did he/she run? This is a simple 1d kinematics acceleration example. Determine the distance traveled before takeoff. T) = 0 from 0 s to 3 s; Determine the distance traveled before takeoff. Web (a) 1 m (b) 2 m (c) 3 m (d) 4m (e) 5 m ans. A runner accelerates to 4.2 m/s2 for 10 seconds before winning the race. Different types of motion we'll look at: A race car can reach a velocity of 75.0 m/s in 3.72s. Different types of motion we'll look at: Web up to 24% cash back time taken (1) 2. An airplane accelerates down a runway at 5.20 m/s2for 32.8 s until it finally lifts off the ground. Determine the displacement from t = 0s to t = 4 s. A person can move very fast and thus have a large speed but. D= v i = v f = a= t= 2. Web web kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Web up to 24% cash back time taken (1) 2. Web kinematic equations solve the following. See answer see solution below. How far did he/she run? Web sci 440u 1 worksheet 1: How far would the same car travel when. Web (a) 1 m (b) 2 m (c) 3 m (d) 4m (e) 5 m ans. Determine the acceleration of the car and the distance traveled. Which one of the following correctly defines both the average velocity and average. Different types of motion we'll look at: Web a race car accelerates uniformly from 18.5 m/s to 46.1 m/s in 2.47 seconds. Web kinematic equations solve the following. D= v i = v f = a= t= 2. A plane starts from rest and accelerates. Different types of motion we'll look at: T) = 0 from 0 s to 3 s; See answer see solution below. Determine the acceleration of the car and the distance traveled. Web web kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Web the solutions guide includes all the pdfs and source documents (ms word files) of the think sheets at the curriculum corner, along with answers, explanations, and solutions,. Determine the displacement from t = 0s to t = 4 s. Web a race car accelerates uniformly from 18.5. T) = 0 from 0 s to 3 s; Web velocity and acceleration in one dimension, the average velocity and acceleration over a time interval ∆t are given by ∆x vavg ∆t and ∆v aavg = ∆t (2.1) the instantaneous. Web web kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. A person can move very fast and thus. Different types of motion we'll look at: Web a race car accelerates uniformly from 18.5 m/s to 46.1 m/s in 2.47 seconds. See answer see solution below. The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final. A person can move very fast and thus have a large speed but if. Which one of the following correctly defines both the average velocity and average. Web up to 24% cash back time taken (1) 2. An airplane accelerates down a runway at 5.20 m/s2for 32.8 s until it finally lifts off the ground. Different types of motion we'll look at: Give a written description of the motion. Determine the acceleration of the car and the distance traveled. Determine the displacement from t = 0s to t = 4 s. Web (a) 1 m (b) 2 m (c) 3 m (d) 4m (e) 5 m ans. Give a written description of the motion. Web sci 440u 1 worksheet 1: What is the acceleration of the car? T) = 0 from 0 s to 3 s; Determine the distance traveled before takeoff. A plane starts from rest and accelerates. Web the three fundamental equations of kinematics in one dimension are: Web kinematics in one dimension 1. This is a simple 1d kinematics acceleration example. The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final. Answer the following based on the velocity vs. Web web kinematic equations relate the variables of motion to one another. Web up to 24% cash back time taken (1) 2. Web kinematics in one dimension 1. Web the three fundamental equations of kinematics in one dimension are: An airplane accelerates down a runway at 5.20 m/s2for 32.8 s until it finally lifts off the ground. How far would the same car travel when. This is a simple 1d kinematics acceleration example. Determine the distance traveled before takeoff. Determine the displacement from t = 0s to t = 4 s. Which one of the following correctly defines both the average velocity and average. Web velocity and acceleration in one dimension, the average velocity and acceleration over a time interval ∆t are given by ∆x vavg ∆t and ∆v aavg = ∆t (2.1) the instantaneous. Particle moves from a point p to a point q in a time t. The variables include acceleration (a), time (t), displacement (d), final. Web sci 440u 1 worksheet 1: A person can move very fast and thus have a large speed but if. A runner accelerates to 4.2 m/s2 for 10 seconds before winning the race. Web kinematic equations solve the following.Kinematics Worksheet With Answers
Acceleration Practice Problems Answer Key
Spice of Lyfe Physics Kinematic Equations Quiz
Spice of Lyfe Physics Kinematic Equations Quiz
1D Kinematics General problems of motion with constant acceleration
(PDF) KINEMATICS TESTS WITH ANSWER KEYS
1d Kinematics Acceleration Worksheet Answers Askworksheet
1d Kinematics Acceleration Worksheet Answers Askworksheet
50 Acceleration Practice Problems Worksheet Chessmuseum Template Library
1d Kinematics Acceleration Worksheet Answers Thekidsworksheet
Web (A) 1 M (B) 2 M (C) 3 M (D) 4M (E) 5 M Ans.
Different Types Of Motion We'll Look At:
Answer The Following Based On The Velocity Vs.
Web Web Kinematic Equations Relate The Variables Of Motion To One Another.
Related Post: