Chapter 12 Solutions Chemistry Worksheet Answers
Chapter 12 Solutions Chemistry Worksheet Answers - Web terms in this set (25) soluble. Web problem 6.1.1.3 determine the molarity for each of the following solutions: A mixture contains 1 mole of volatile liquid a (p oa =100 mm hg) and 3 moles of volatile liquid b (p. Match the type of mixture on the left to its. Homogenous mixture of two or more substances in a single phase. Mass and atoms are conserved. The solvent is the component. In a solution, the ______ is the largest amount and the _______ is the smallest amount?. Will the difference between the two be greater for a dilute or a. The dissolving medium in a solution. Web the relative number of moles of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Web solutes that dissolve to form molecules that don't conduct electricity. Web chapter 12 review solutions section 1 short answer answer the following questions in the space provided. Web problem 6.1.1.3 determine the molarity for each of the following solutions: The other end of the string. Web problem 6.1.1.3 determine the molarity for each of the following solutions: 0.444 mol of cocl 2 in 0.654 l of solution 98.0 g of phosphoric acid, h 3 po. The sum of the changes of enthalpy in each step of the formation of a solution. Water and alcohol are examples of. Mass and atoms are conserved. Web terms in this set (25) soluble. Mass and atoms are conserved. Will the difference between the two be greater for a dilute or a. Web explain why the molality and molarity of an aqueous solution are not always numerically identical. Homogenous mixture of two or more substances in a single phase. If a system of equations has three equations and four unknowns, then it could have a unique. Our resource for chemistry includes answers to chapter. Factors that affect the rate of. The sum of the changes of enthalpy in each step of the formation of a solution. Homogenous mixture of two or more substances in a single phase. The oxidation of haircolor is an example of a physical change. Web our resource for modern chemistry includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. Enthalpy change that occurs when 1 mol of the gaseous. A mixture contains 1 mole of volatile liquid a (p oa =100 mm hg). Web an air puck of mass m 1 m_1 m 1 is tied to a string and allowed to revolve in a circle of radius r r r on a frictionless horizontal table. Web determine whether each of the following statements is true or false, and explain why. They are homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. Factors that. Web these free worksheets are based on the latest cbse ncert books and syllabus and cover all relevant questions and answers in class 12 chemistry. Web an air puck of mass m 1 m_1 m 1 is tied to a string and allowed to revolve in a circle of radius r r r on a frictionless horizontal table. The solvent. Mass and atoms are conserved. Water and alcohol are examples of. Web problem 6.1.1.3 determine the molarity for each of the following solutions: The sum of the changes of enthalpy in each step of the formation of a solution. What is the compound’s molar mass if 6.21 g of it is dissolved in 24.0 g of chcl 3 from a. Factors that affect the rate of. The dissolving medium in a solution. Web the relative number of moles of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Web terms in this set (25) soluble. Web problem 6.1.1.3 determine the molarity for each of the following solutions: 0.444 mol of cocl 2 in 0.654 l of solution 98.0 g of phosphoric acid, h 3 po. Our resource for chemistry includes answers to chapter. Web solutes that dissolve to form molecules that don't conduct electricity. Web determine whether each of the following statements is true or false, and explain why. Web these free worksheets are based on the. Web explain why the molality and molarity of an aqueous solution are not always numerically identical. Web chapter 12 review solutions section 1 short answer answer the following questions in the space provided. They are homogeneous mixtures of two or more pure substances. Web terms in this set (25) soluble. Web problem 6.1.1.3 determine the molarity for each of the following solutions: Permanent mixture of two or more substances that are united with the aid of a binder. Will the difference between the two be greater for a dilute or a. Web these free worksheets are based on the latest cbse ncert books and syllabus and cover all relevant questions and answers in class 12 chemistry. Water and alcohol are examples of. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more components. What is the compound’s molar mass if 6.21 g of it is dissolved in 24.0 g of chcl 3 from a. The solvent is the component. The other end of the string passes through. Our resource for chemistry includes answers to chapter. The dissolving medium in a solution. The laws of conservation of mass. In a solution, the ______ is the largest amount and the _______ is the smallest amount?. Web determine whether each of the following statements is true or false, and explain why. Web the relative number of moles of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Mass and atoms are conserved. Web problem 6.1.1.3 determine the molarity for each of the following solutions: The solvent is the component. The dissolving medium in a solution. In a solution, the ______ is the largest amount and the _______ is the smallest amount?. What is the compound’s molar mass if 6.21 g of it is dissolved in 24.0 g of chcl 3 from a. Permanent mixture of two or more substances that are united with the aid of a binder. The oxidation of haircolor is an example of a physical change. Web determine whether each of the following statements is true or false, and explain why. Web the relative number of moles of reactants and products in a chemical reaction. The laws of conservation of mass. Factors that affect the rate of. Web solutes that dissolve to form molecules that don't conduct electricity. Web our resource for modern chemistry includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more components. Web explain why the molality and molarity of an aqueous solution are not always numerically identical. The sum of the changes of enthalpy in each step of the formation of a solution.Ncert Solution For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones
Chemistry Notes For Class 12 Chapter 2 Solutions Solution Osmosis
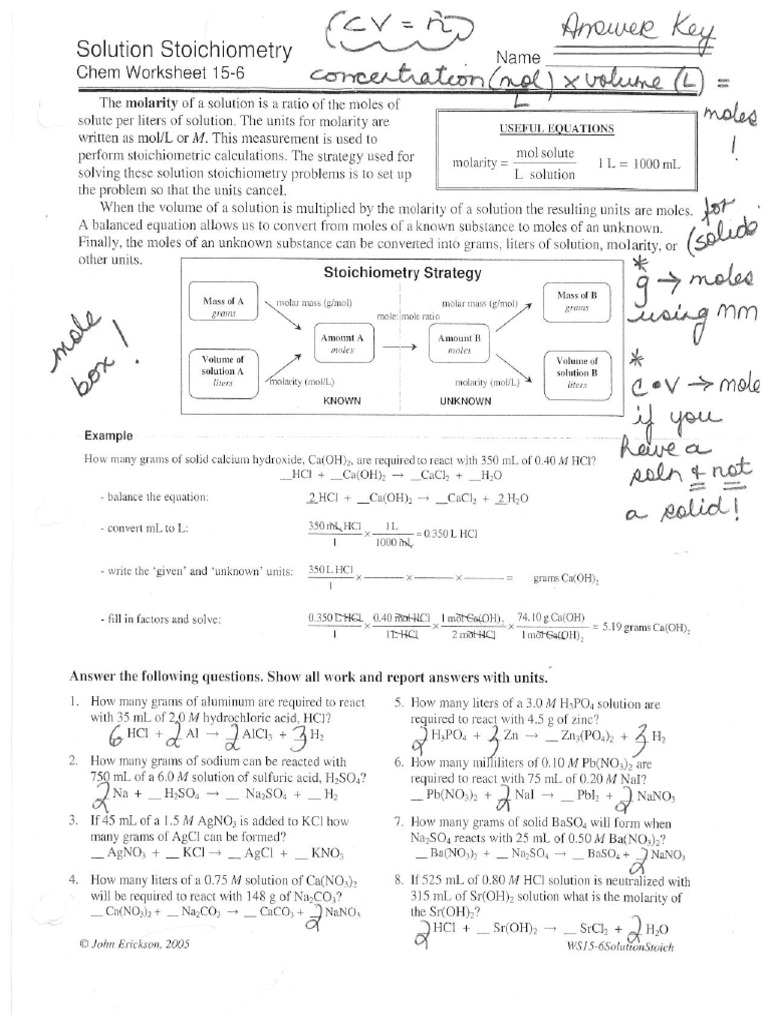
Stoichiometry Practice Worksheet Answer Key
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Solutions Chapter 12 Aldehydes
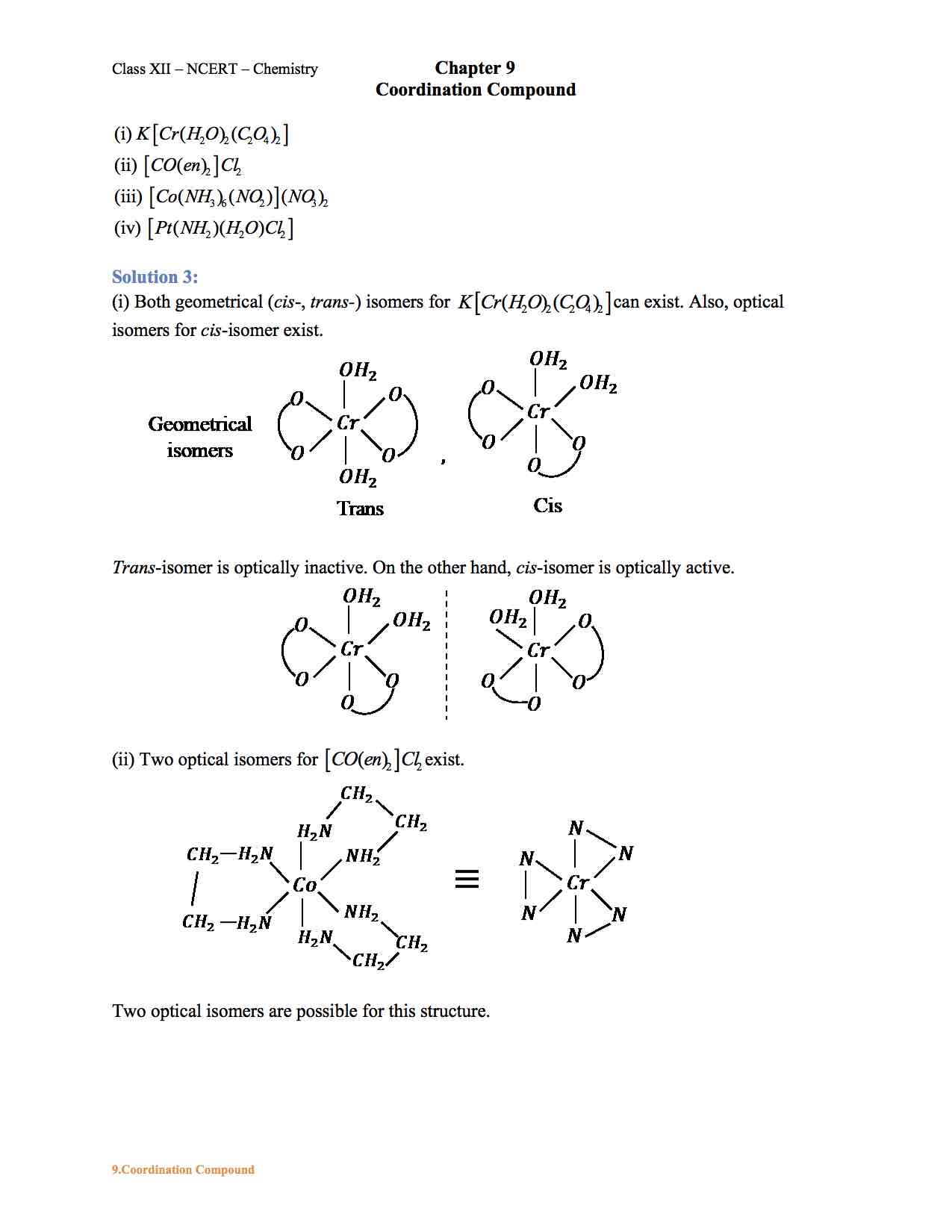
Ncert Solution For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry Solutions Chapter 10 Haloalkanes
Chapter 6 The Periodic Table Worksheet Answers Pearson
Balancing Chemical Equations Worksheet With Answers Grade 10 A
Chemistry
Formula of Class 12 Chapter Liquid Solutions PW
Match The Type Of Mixture On The Left To Its.
Mass And Atoms Are Conserved.
Web An Air Puck Of Mass M 1 M_1 M 1 Is Tied To A String And Allowed To Revolve In A Circle Of Radius R R R On A Frictionless Horizontal Table.
Web Chapter 12 Review Solutions Section 1 Short Answer Answer The Following Questions In The Space Provided.
Related Post: