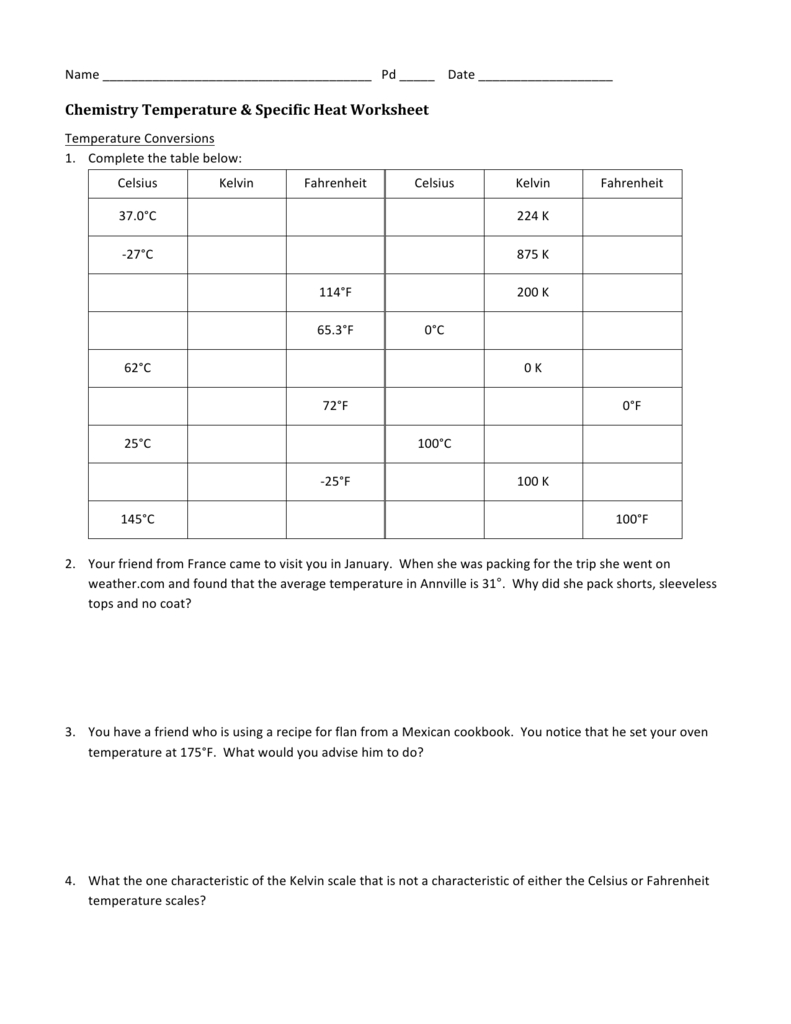
Chemistry Specific Heat Worksheet
Chemistry Specific Heat Worksheet - They will also see the effect that a catalyst has on activation energy. Web q = m × c s × δt. C = t/m ̈t, zheue t = heaw eneug, m = mavv, and t = wempeuawxue remembeu, ̈t =(tfinal ± tinitial). 3) which will heat up slower> explain why. This high school chemistry inquiry activity walks students through a. Web substance specific heat capacity (j/g °c) water 4.18 j/g °c aluminum 0.89 j/g °c silicon 0.7 3 j/g °c iron 0.45 j/g °c copper 0.387 j/g °c silver 0.24 j/g °c gold 0.129 j/ °c lead. It measures how much energy (in joules) is required to raise one gram of a substance by one degree celsius. Specific heat is a measure of how much energy is needed to change the. Web understand the concepts of heat capacity, molar heat capacity, and specific heat; How many joules of heat are. What equations must be used to calculate the heat associated with a phase change? Web what was the final temperature of the gold? Web where the mass, specific heat, and change in temperature are multiplied together. Use q = (m)(cp))(δt) to solve the following problems. A total of 54.0 joules of heat are absorbed as 58.3 g of lead is. Understand the principles of calorimetry; Web substance specific heat capacity (j/g °c) water 4.18 j/g °c aluminum 0.89 j/g °c silicon 0.7 3 j/g °c iron 0.45 j/g °c copper 0.387 j/g °c silver 0.24 j/g °c gold 0.129 j/ °c lead. In this worksheet, students will. Show all work and proper units. Web remember that specific heat, cp, is. From these data, what is the specific. Why can’t the specific heat equation be used? Web specific heat of iridium example problem. Web the specific heat of a substance can be used to calculate the temperature change that a given substance will undergo when it is either heated or cooled. In this worksheet, students will. Web q = m × c s × δt. 3) which will heat up slower> explain why. They will also see the effect that a catalyst has on activation energy. Web the specific heat of a substance can be used to calculate the temperature change that a given substance will undergo when it is either heated or cooled. It measures. Use q = (m)(cp))(δt) to solve the following problems. Web where the mass, specific heat, and change in temperature are multiplied together. Csh = q/m∆t, where q = heat energy, m = mass, and t = temperature. Heat capacity of substances q = s m δt = c δt heat (q) absorbed depends on specific heat capacity, mass and temperature.. Web specific heat and heat capacity worksheet directions: 𝐽 2) define specific heat and provide the units for it. Web what was the final temperature of the gold? (remember the specific heat of water is 1. Web where the mass, specific heat, and change in temperature are multiplied together. Web remember that specific heat, cp, is the amount of heat required to raise one gram of a substance by one degree celsius. Web specific heat of iridium example problem. Web understand the concepts of heat capacity, molar heat capacity, and specific heat; Why can’t the specific heat equation be used? What equations must be used to calculate the heat. This high school chemistry inquiry activity walks students through a. Web remember that specific heat, cp, is the amount of heat required to raise one gram of a substance by one degree celsius. Show all work and units. 𝐽 2) define specific heat and provide the units for it. Specific heat is a measure of how much energy is needed. Web substance specific heat capacity (j/g °c) water 4.18 j/g °c aluminum 0.89 j/g °c silicon 0.7 3 j/g °c iron 0.45 j/g °c copper 0.387 j/g °c silver 0.24 j/g °c gold 0.129 j/ °c lead. From these data, what is the specific. Why can’t the specific heat equation be used? Web the specific heat of a substance can. Web the specific heat of a substance can be used to calculate the temperature change that a given substance will undergo when it is either heated or cooled. This high school chemistry inquiry activity walks students through a. It measures how much energy (in joules) is required to raise one gram of a substance by one degree celsius. Heat capacity. Understand the principles of calorimetry; Web specific heat and heat capacity worksheet; It measures how much energy (in joules) is required to raise one gram of a substance by one degree celsius. Use q = (m)(cp))(δt) to solve the following problems. Web the specific heat of a substance can be used to calculate the temperature change that a given substance will undergo when it is either heated or cooled. This high school chemistry inquiry activity walks students through a. Web in this worksheet, students will look at enthalpy graphs and measure the activation energy of a reaction. Web what was the final temperature of the gold? C = t/m ̈t, zheue t = heaw eneug, m = mavv, and t = wempeuawxue remembeu, ̈t =(tfinal ± tinitial). How many joules of heat are. Show all work and proper units. Web understand the concepts of heat capacity, molar heat capacity, and specific heat; What equations must be used to calculate the heat associated with a phase change? Csh = q/m∆t, where q = heat energy, m = mass, and t = temperature. Show all work and units. Show all work and proper units. Web specific heat and heat capacity worksheet directions: Web specific heat of iridium example problem. (remember the specific heat of water is 1. Heat capacity of substances q = s m δt = c δt heat (q) absorbed depends on specific heat capacity, mass and temperature. Web q = m × c s × δt. Web specific heat of iridium example problem. Specific heat is a measure of how much energy is needed to change the. How many calories of heat are required to raise the temperature of 550 g of water from 12 to 18? Web substance specific heat capacity (j/g °c) water 4.18 j/g °c aluminum 0.89 j/g °c silicon 0.7 3 j/g °c iron 0.45 j/g °c copper 0.387 j/g °c silver 0.24 j/g °c gold 0.129 j/ °c lead. Web specific heat and heat capacity worksheet directions: Understand the principles of calorimetry; What equations must be used to calculate the heat associated with a phase change? It measures how much energy (in joules) is required to raise one gram of a substance by one degree celsius. In this worksheet, students will. Web where the mass, specific heat, and change in temperature are multiplied together. Use q = (m)(cp))(δt) to solve the following problems. Why can’t the specific heat equation be used? They will also see the effect that a catalyst has on activation energy. Web specific heat is a physical property. 3) which will heat up slower> explain why.Specific Heat Chem Worksheet 16 1 Answer Key —
PWHS Thermodynamics Specific Heat Worksheet
Specific Heat Chem Worksheet 16 1 Answer Key —
Worksheet Calculations Involving Specific Heat
Specific Heat Worksheet Heat Thermodynamic Properties
specific heat chemistry worksheet
15 Best Images of Specific Heat Worksheet Answer Key Specific Heat
Chemistry Temperature Specific Heat Worksheet —
Heat Capacity and Specific Heat Worksheet 1 3/3/04 12641 PM
Specific Heat Worksheet Answer Key
Show All Work And Units.
This Is An Intensive Physical Property And Has Been.
Web Specific Heat Is The Amount Of Heat Needed To Raise The Temperature Of 1 Gram Of A Substance By 1 Degree Celsius.
Web Understand The Concepts Of Heat Capacity, Molar Heat Capacity, And Specific Heat;
Related Post: