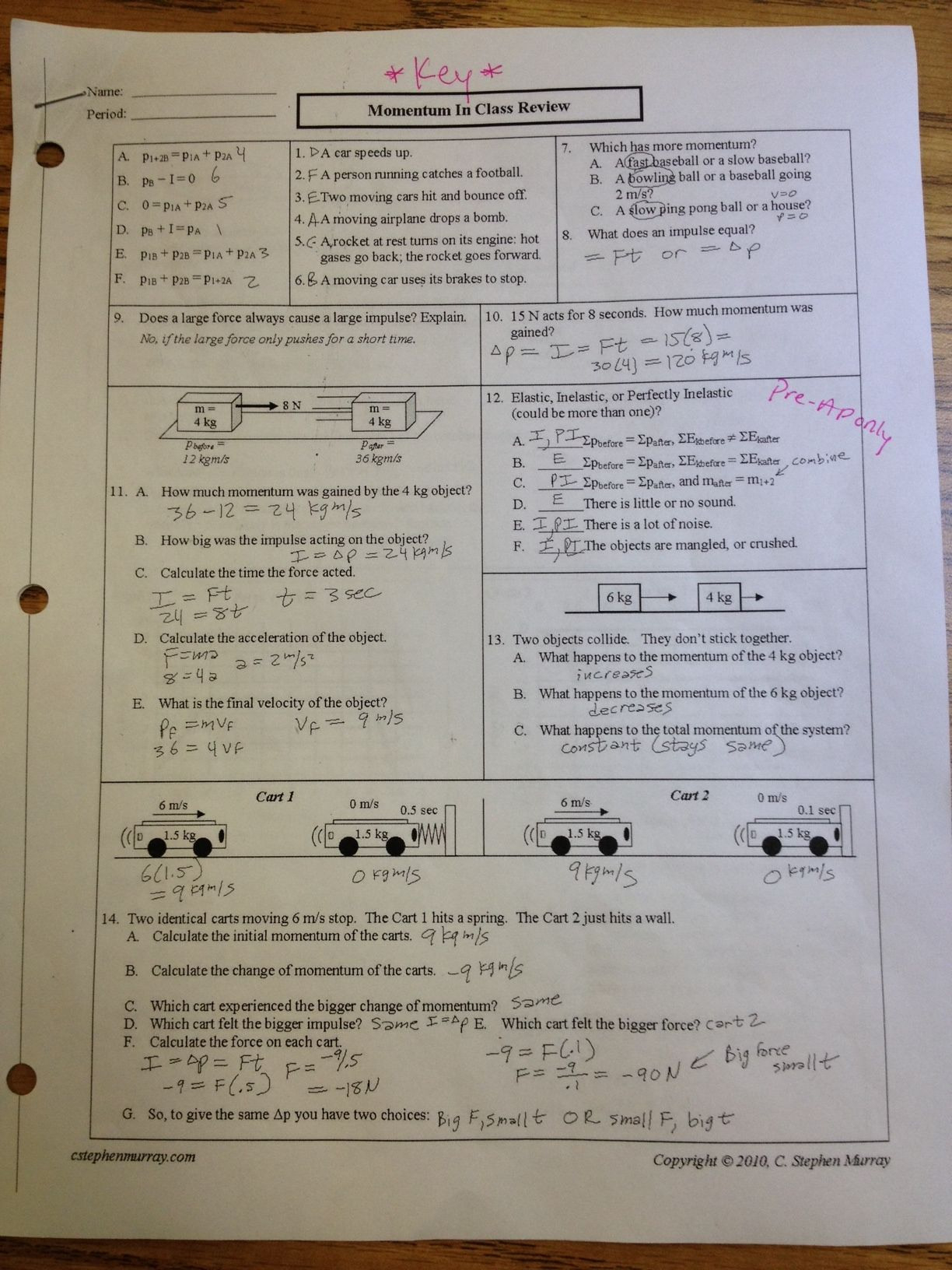
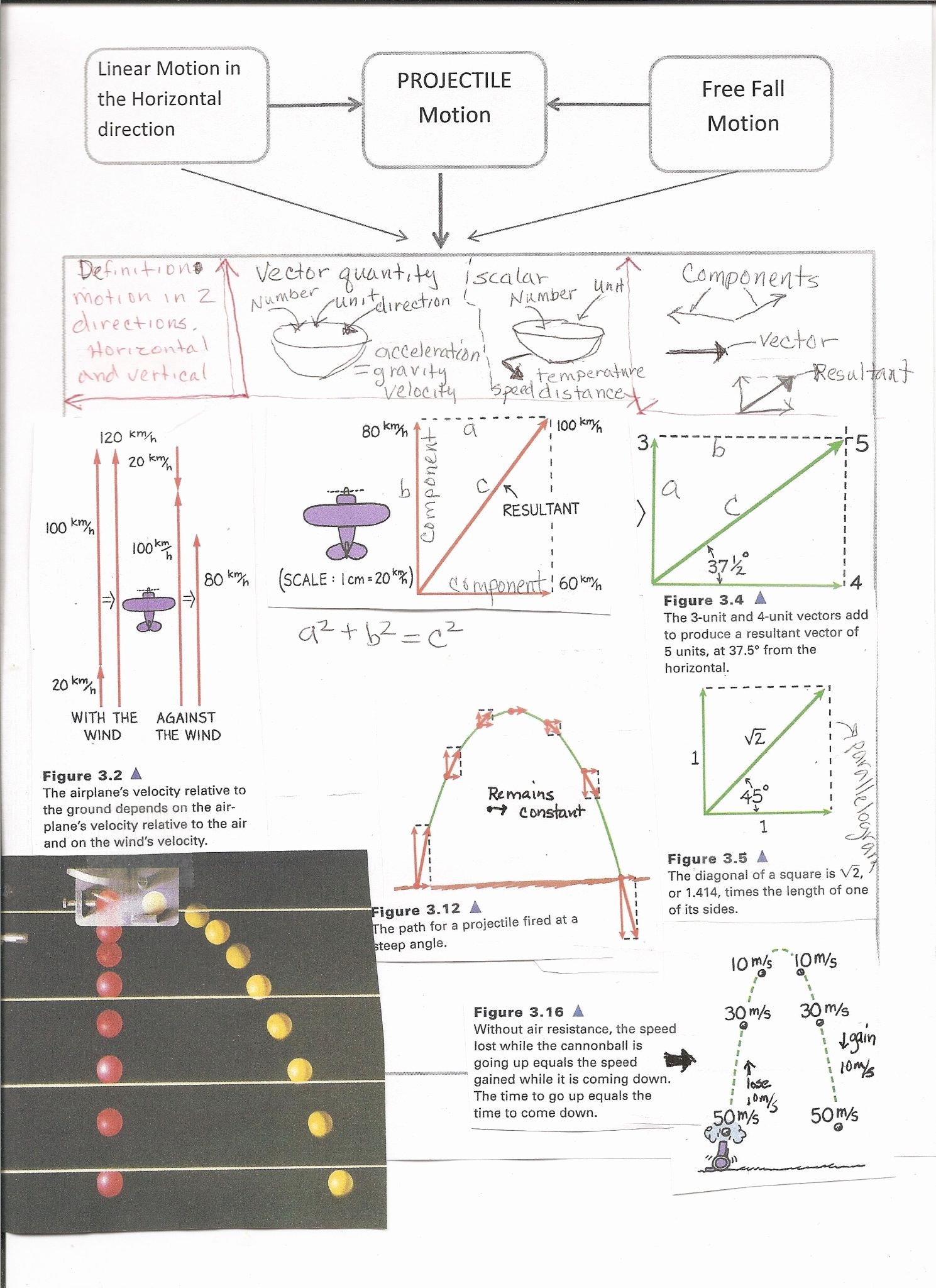
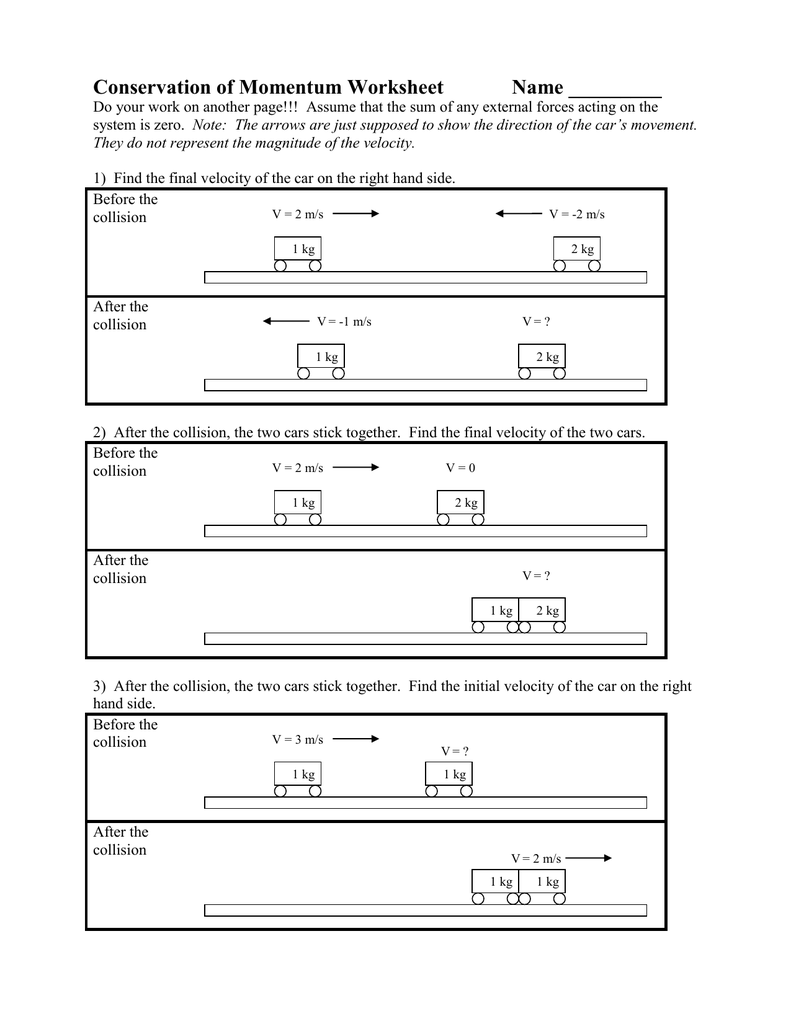
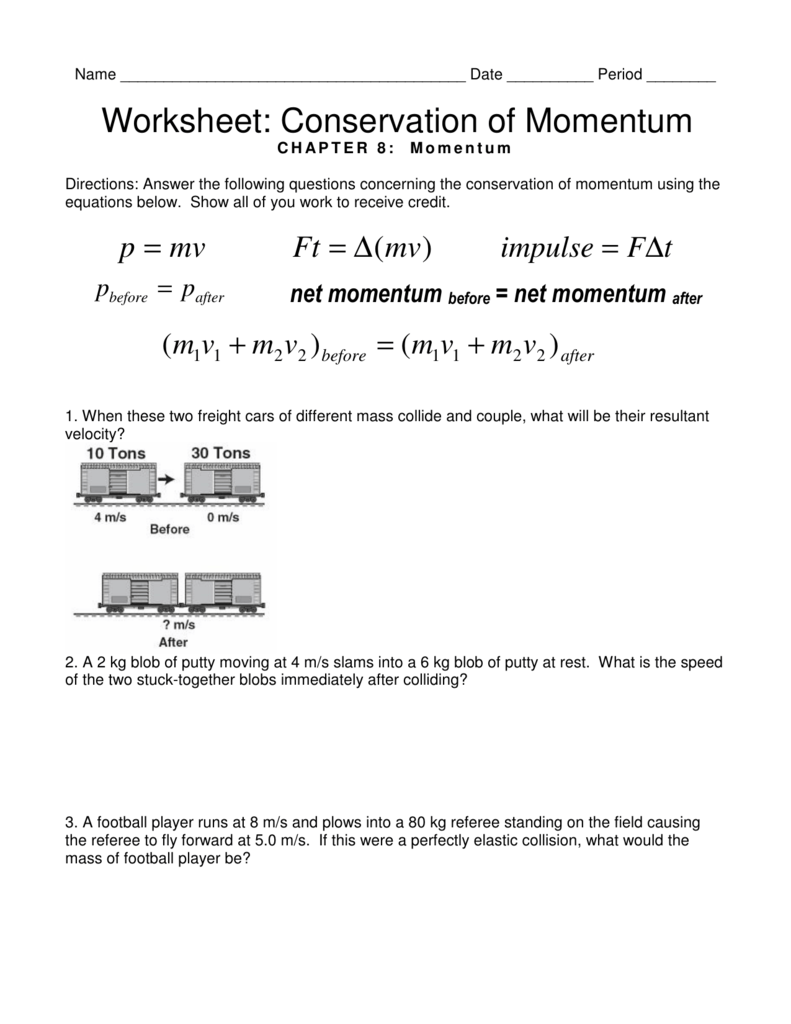
Collisions Momentum Worksheet 4 Answer Key
Collisions Momentum Worksheet 4 Answer Key - Web solve collision problems by applying the law of conservation of momentum section key terms elastic and inelastic collisions when objects collide, they can either stick together or bounce off one another, remaining separate. Determine the final velocity of the object. V f = 13.5 m/s; V i = 18.0 m/s; With newpathworksheets printable guides & worksheets, students easily understand this topic. Kg•m/s = (4.88 kg)•v + 4.93. (a) impulse, (b) force (a) whim = momentum cha Web the physical topic of momentum and collisions will not be a challenge. Assuming that these two balls have a head on collision and stick together, what will be the final velocity of the combination? Momentum collisions 2d (matt) 18. A golfer strikes a golf ball of mass 0.05 kg, and the time of impact between the golf club and the ball is 1.0 ms. A 0.45 caliber bullet (m = 0.162 kg) leaving the muzzle of a gun at 860 m/s. Two trains, big red and little blue, have. V i = 18.0 m/s; Web 3 worksheets with over. Momentum collisions 2d (matt) 18. V f = 13.5 m/s; (a) stimulus, (b) force (a) impulse = momentum ch A 12.0 kg mass is moving to the left with a velocity of 5.00 m/s. Web solve collision problems by applying the law of conservation of momentum section key terms elastic and inelastic collisions when objects collide, they can either stick. Multiple versions can be used for review, extra. V f = 13.5 m/s; Phoebe i = 18.0 m/s; Momentum collisions 2d (matt) 18. Elastic collision (hard way) 11. A golfer strikes a golf ball of mass 0.05 kg, and the time of impact between the golf club and the ball is 1.0 ms. If the ball acquires a velocity of magnitude 70 m/s, calculate the average force exerted on the ball. If the time of impact in a collision is extended by. How is the resulting change in. A golfer strikes a golf ball of mass 0.05 kg, and the time of impact between the golf club and the ball is 1.0 ms. A resistive force of 6.0 n then impedes its motion for 8.0 seconds. Fin i = 18.0 m/s; Web conservation of momentum aviaries. Web the physical topic of momentum and collisions will not be a. Phoebe i = 18.0 m/s; (a) impulse, (b) force (a) whim = momentum cha Assuming that these two balls have a head on collision and stick together, what will be the final velocity of the combination? If the ball acquires a velocity of magnitude 70 m/s, calculate the average force exerted on the ball. Kg•m/s = (4.88 kg)•v + 4.93. For a constant force, if the duration of impact upon an object is doubled, how is the impulse affected? Assuming that these two balls have a head on collision and stick together, what will be the final velocity of the combination? V i = 18.0 m/s; Momentum collisions 2d (matt) 18. Elastic collision (hard way) 11. If the time of impact in a collision is extended by. A resistive force of 6.0 n then impedes its motion for 8.0 seconds. Fin i = 18.0 m/s; (a) stimulus, (b) force (a) impulse = momentum ch Momentum collisions 2d (matt) 18. With newpathworksheets printable guides & worksheets, students easily understand this topic. If the ball acquires a velocity of magnitude 70 m/s, calculate the average force exerted on the ball. V f = 13.5 m/s; Web solve collision problems by applying the law of conservation of momentum section key terms elastic and inelastic collisions when objects collide, they can either stick. N•s impulse acts upon it in the direction of motion for 5.0 seconds. V f = 13.5 m/s; (a) stimulus, (b) force (a) impulse = momentum ch If the ball acquires a velocity of magnitude 70 m/s, calculate the average force exerted on the ball. Web conservation of momentum aviaries. V f = 13.5 m/s; Elastic collision (hard way) 11. A 0.45 caliber bullet (m = 0.162 kg) leaving the muzzle of a gun at 860 m/s. Web 3 worksheets with over 30 questions extensively covering the principle of conservation of momentum, elastic collision, inelastic collision, explosion, frinctional force, balanced forces, impulse and impulsive force. (a) impulse, (b) force (a) urge = momentu Web conservation of momentum aviaries. Web solve collision problems by applying the law of conservation of momentum section key terms elastic and inelastic collisions when objects collide, they can either stick together or bounce off one another, remaining separate. A 9.00 kg mass is moving to the right with a velocity of 14.0 m/s. A 12.0 kg mass is moving to the left with a velocity of 5.00 m/s. Web all problems are algorithm driven so each version has shuffled answers, numbers, and variables. N•s impulse acts upon it in the direction of motion for 5.0 seconds. Multiple versions can be used for review, extra. Determine the final velocity of the object. Kg•m/s = (4.88 kg)•v + 4.93. If the ball acquires a velocity of magnitude 70 m/s, calculate the average force exerted on the ball. Two trains, big red and little blue, have. For a constant force, if the duration of impact upon an object is doubled, how is the impulse affected? V f = 13.5 m/s; A golfer strikes a golf ball of mass 0.05 kg, and the time of impact between the golf club and the ball is 1.0 ms. (4.88 kg)•(2.41 m/s) = (4.88 kg)•v + (0.95 kg)•(5.19 m/s) 11.76. N•s impulse acts upon it in the direction of motion for 5.0 seconds. Assuming that these two balls have a head on collision and stick together, what will be the final velocity of the combination? Ice skater throws ball 14. V i = 18.0 m/s; In this section, we’ll cover these two. A 12.0 kg mass is moving to the left with a velocity of 5.00 m/s. Fin i = 18.0 m/s; For a constant force, if the duration of impact upon an object is doubled, how is the impulse affected? Web the physical topic of momentum and collisions will not be a challenge. Web 3 worksheets with over 30 questions extensively covering the principle of conservation of momentum, elastic collision, inelastic collision, explosion, frinctional force, balanced forces, impulse and impulsive force. Two trains, big red and little blue, have. A 9.00 kg mass is moving to the right with a velocity of 14.0 m/s. Web conservation of momentum aviaries. Phoebe i = 18.0 m/s; If the ball acquires a velocity of magnitude 70 m/s, calculate the average force exerted on the ball. V f = 13.5 m/s;Unlock The Secrets Of Collision Momentum With Worksheet 4 Answer Key
momentum and collisions worksheet answers
Collisions Momentum Worksheet 4 Answers —
50 Momentum Worksheet Answer Key Chessmuseum Template Library
30 Momentum Worksheet Answer Key Education Template
Unlock The Secrets Of Collision Momentum With Worksheet 4 Answer Key
Collisions Momentum Worksheet 4 Answers —
Momentum And Collisions Worksheet Answer Key Ivuyteq
10++ Collisions Momentum Worksheet 4 Answer Key
Momentum Worksheet Answer Key
How Is The Resulting Change In Momentum Affected?
Multiple Versions Can Be Used For Review, Extra.
Determine The Final Velocity Of The Object.
Kg•M/S = (4.88 Kg)•V + 4.93.
Related Post: