Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3 Position Vs Time Graphs
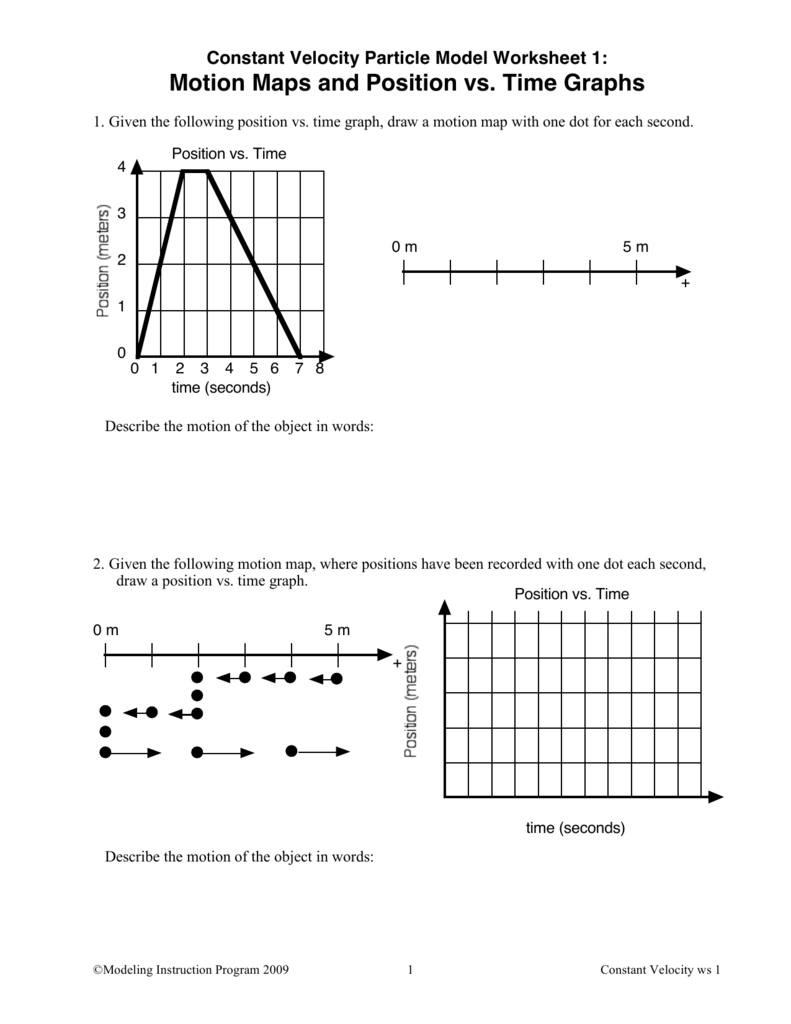
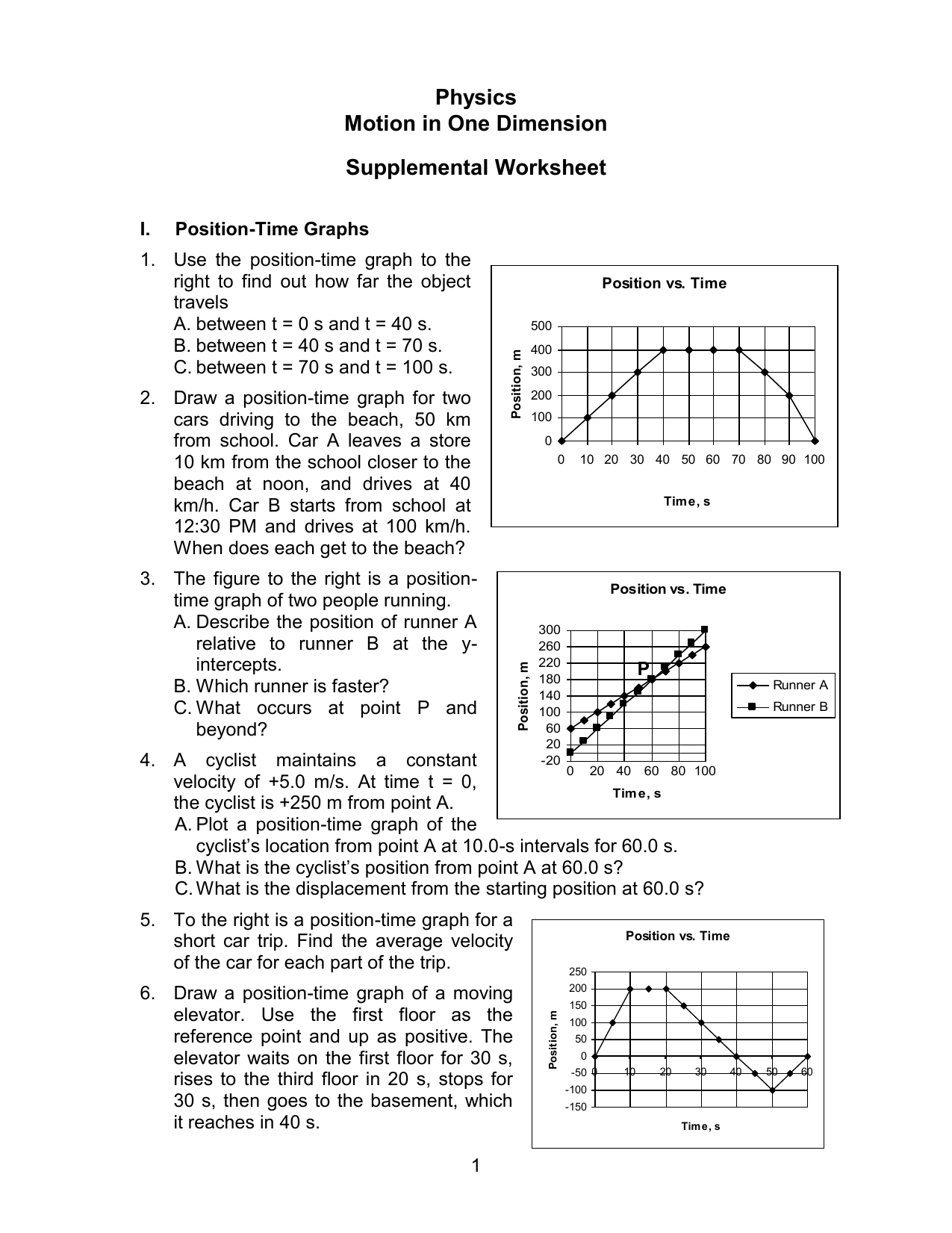
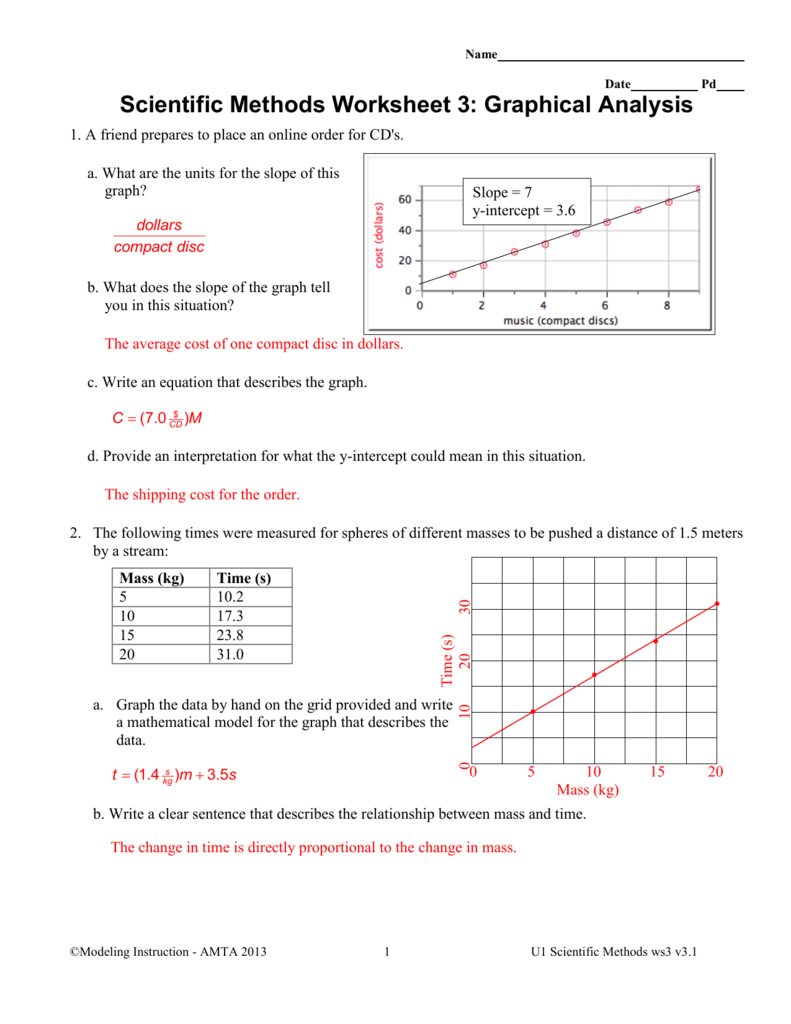
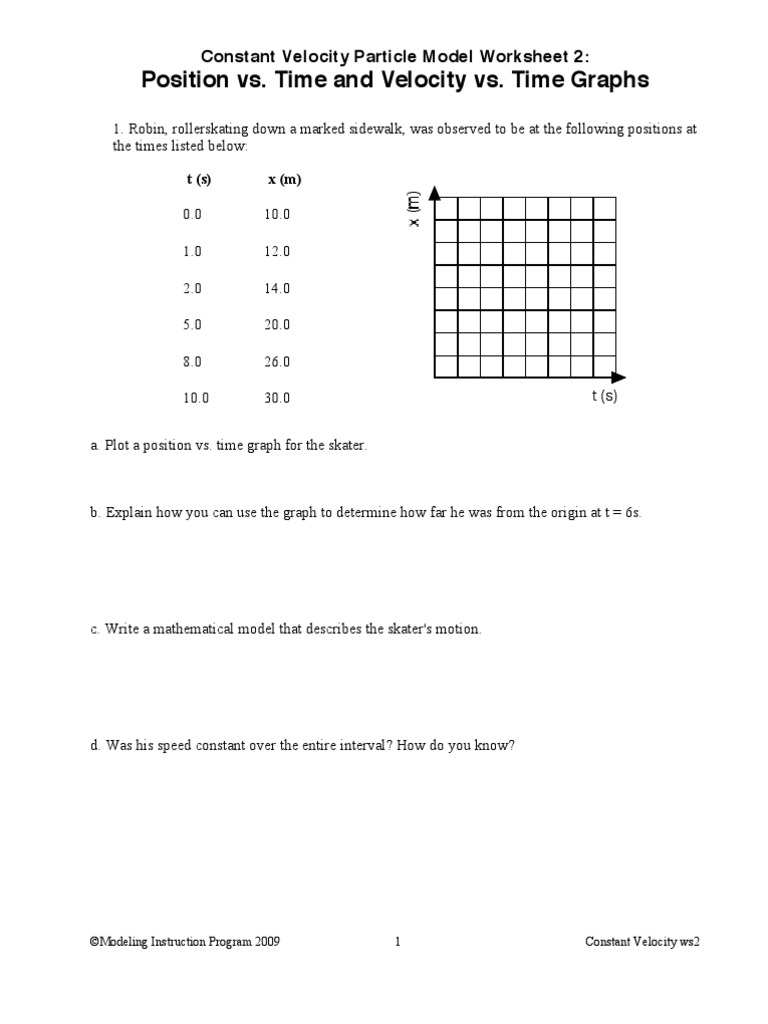
Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3 Position Vs Time Graphs - At t= 7s, which cyclist is ahead? Time graphs sketch velocity vs. Time graph below for cyclists a and b. The object is moving in the positive direction at a constant (steady) speed. (average velocity is the displacement (final position minus initial position) divided by time elapsed.) determine the skater's average speed from t = 0s to t = 16s. Web sketch the velocity vs time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object. Mathematical model from x vs t graph for constant velocity. Time graphs pd given the following position vs. Web how do you know? Time 0 m 5 m + 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8time (seconds) describe the motion of the object in words: If not, which is ahead? Web the slope of a horizontal position versus time graph gives you the velocity in the x direction. Time graphs and motion maps corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object. Time graph, draw a motion map with one dot for each second. The average slope gives you the average velocity. X vs t graph for object moving forward with constant velocity. Time graph, draw a motion map with one dot for each second. Calculate the slope of the line on the x. Determine the skater's average velocity from t = 0s to t = 16s. Motion maps and velocity vs. The object is moving in the positive direction at a constant (steady) speed. Determine the skater's average velocity from t = 0s to t = 16s. Web how do you know? Time graphs name date pd constant velocity particle model worksheet 3: Time graph for the skater. Time 0 m 5 m + 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8time (seconds) describe the motion of the object in words: The object is moving away from the origin at a constant velocity. Which cyclist is traveling faster at 3s? Web constant velocity particle model worksheet 1: Robin, rollerskating down a marked sidewalk, was observed to be. Motion maps and position vs. Time graph, draw a motion map with one dot for each second. Time graphs sketch velocity vs. If not, which is ahead? Web constant velocity particle model worksheet 2: Web up to $3 cash back constant velocity particle model worksheet 2: Motion maps and position vs. X vs t graph for object moving forward with constant velocity. Time graphs and motion maps corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object. (average velocity is the displacement (final position minus initial position) divided by time elapsed.) determine the. X vs t graph for object moving forward with constant velocity. Web sketch the velocity vs time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object. (average velocity is the displacement (final position minus initial position) divided by time elapsed.) determine the skater's average speed from t = 0s to t = 16s. Web it is the. If not, which is ahead? (average velocity is the displacement (final position minus initial position) divided by time elapsed.) determine the skater's average speed from t = 0s to t = 16s. Robin, rollerskating down a marked sidewalk, was observed at the following positions at the times listed below: The object is standing still. Explain how you can use the. If not, which is ahead? Given the following position vs. The object is standing still. The object is moving in the positive direction at a constant (steady) speed. Time graph, draw a motion map with one dot for each second. Robin, rollerskating down a marked sidewalk, was observed at the following positions at the times listed below: If not, which is ahead? Time graph below for cyclists a and b. The object is moving in the positive direction at a constant (steady) speed. Web it is the average velocity over the interval of time the slope is taken b. Web constant velocity particle model worksheet 2: Do the cyclists start at the same point? The object is moving in the positive direction at a constant (steady) speed. Explain how you can use the graph to determine how far he was from the origin at t = 6.0s. X vs t graph for object moving backward with constant velocity. Motion maps and velocity vs. Time graphs pd given the following position vs. X vs t graph for object moving forward with constant velocity. The object is moving away from the origin at a constant velocity. T (s) x (m) 0.0 10.0 1.0 12.0 2.0 14.0 5.0 20.0 8.0 26.0 The object is standing still. Time graph, draw a motion map with one dot for each second. Web constant velocity particle model worksheet 1: Web sketch the velocity vs time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object. 0 m + time 2. Mathematical model from x vs t graph for constant velocity. Time graphs sketch velocity vs. Web up to 24% cash back constant velocity particle model worksheet 3: (average velocity is the displacement (final position minus initial position) divided by time elapsed.) determine the skater's average speed from t = 0s to t = 16s. Time graph below for cyclists a and b. Time graphs and motion maps corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object. Time graph for the skater. Web constant velocity particle model worksheet 2: Web it is the average velocity over the interval of time the slope is taken b. If not, which is ahead? The object is moving away from the origin at a constant velocity. If not, which is ahead? Web sketch the velocity vs time graphs corresponding to the following descriptions of the motion of an object. Web the slope of a horizontal position versus time graph gives you the velocity in the x direction. Robin, rollerskating down a marked sidewalk, was observed to be at the following positions at the times listed below: Motion maps and position vs. Time graph, draw a motion map with one dot for each second. At t= 7s, which cyclist is ahead? Robin, rollerskating down a marked sidewalk, was observed to be at the following positions at the times listed below: Web constant velocity particle model worksheet 1: Mathematical model from x vs t graph for constant velocity.Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3 Position Vs Time Graphs
Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3 Position Vs Time Graphs
Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3 Position Vs Time Graphs
Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3 Position Vs Time Graphs
30 Speed Vs Time Graph Worksheet support worksheet
Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3 Position Vs Time Graphs
Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 2
Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 5
Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3 Position Vs Time Graphs
Constant Velocity Particle Model Worksheet 3 Position Vs Time Graphs
The Average Slope Gives You The Average Velocity.
Motion Maps And Velocity Vs.
0 M + Time 2.
Explain How You Can Use The Graph To Determine How Far He Was From The Origin At T = 6.0S.
Related Post: