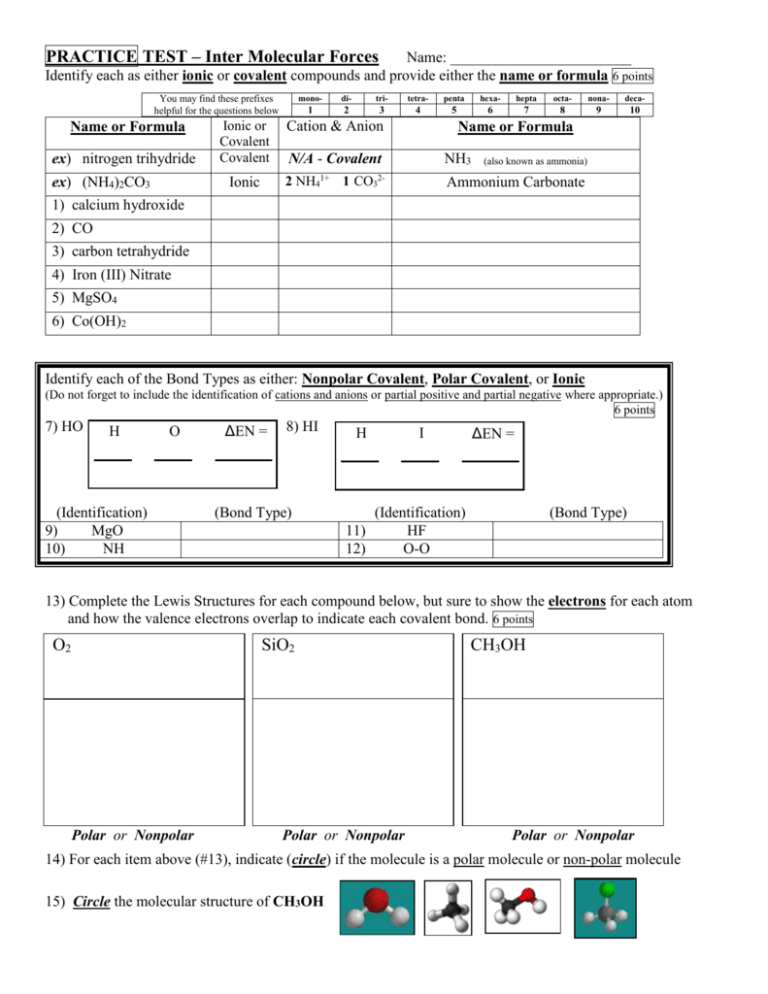
Intermolecular Forces Practice Worksheet
Intermolecular Forces Practice Worksheet - Compare the relative amounts of energy involved in the forming and breaking of these forces. Tell what type of intermolecular force is important in converting each of the following from a gas to a liquid (a) co2; Include in your explanation how they work on the submicroscopic level. You may find it useful to draw lewis structures for some of these molecules: Choose an answer and hit. How are boiling points affected by intermolecular forces? Web print intermolecular forces in chemistry: What holds the two f atoms together in diatomic fluorine? If the intermolecular forces in a liquid increase the normal boiling point of the liquid will_____. Web explain the intermolecular forces that compete to determine whether or not an ionic substance will dissolve in water. Intermolecular forces worksheet answers for each of the following compounds, determine the main intermolecular force. Choose an answer and hit. Web intermolecular forces, ionic bond strength, phase diagrams, heating curves. Describe the three types of intermolecular forces. _types of solids intermolecular force(s) between particles_* 1. Web electrostatics and moments of fixed charge distributions. Web more chemistry tutorials and practice can be found at www.chemfiesta.com. Web explain the intermolecular forces that compete to determine whether or not an ionic substance will dissolve in water. Rank the lattice energy (ionic bond strength) for the following formulas, 1 being strongest: Rank the ionic bond strength for the following. Which of these has only london forces? Answer the following questions with “increase,” “not change,” or “decrease.” a. Web chemistry unit 4 compounds name: Web more chemistry tutorials and practice can be found at www.chemfiesta.com. This molecule is nonpolar because of symmetry. What holds the two f atoms together in diatomic fluorine? What holds molecules of fluorine together? Answer the following questions with “increase,” “not change,” or “decrease.” a. What holds nacl(aq) together in salt water? Coulomb’s law states that the interaction between two charged particles is stronger the larger the charges and the closer they are together. Web understand the effects of strengths of intermolecular forces on phase changes and substance properties such as viscosity and surface tension. This molecule is nonpolar because of symmetry. Which of these has only london forces? Web google classroom in the vapor phase, formic acid exists as dimers (complexes consisting of two formic acid molecules) rather than individual molecules. What holds. Even though the bonds are polar they point in opposite directions so the bond dipoles cancel each other out. Rank the lattice energy (ionic bond strength) for the following formulas, 1 being strongest: Stronger intermolecular forces between molecules make it more difficult for those molecules to be pulled apart. What hold the o and h atoms together in a molecule. Web understand the effects of strengths of intermolecular forces on phase changes and substance properties such as viscosity and surface tension. You may find it useful to draw lewis structures for some of these molecules: Include in your explanation how they work on the submicroscopic level. Web intermolecular forces, ionic bond strength, phase diagrams, heating curves. Web chapter 10 practice. Web in this activity worksheet, students will examine the intermolecular forces between covalent molecules including: Web intermolecular forces are attractions between molecules and will occur over a greater distance than attractions between atoms in a chemical bond. Equal sharing of electrons within the covalent bonds of a molecule results in a _____ molecule. Web electrostatics and moments of fixed charge. Choose an answer and hit. Tell what type of intermolecular force is important in converting each of the following from a gas to a liquid (a) co2; Which of the following diagrams correctly represents the hydrogen bonding (denoted by dotted lines) in the formic acid dimer? Which of these has only london forces? Explain the difference between a chemical bond. Even though the bonds are polar they point in opposite directions so the bond dipoles cancel each other out. This molecule is nonpolar because of symmetry. Compare the relative amounts of energy involved in the forming and breaking of these forces. What holds molecules of fluorine together? Web intermolecular force(s) that are involved. What holds nacl(aq) together in salt water? Even though the bonds are polar they point in opposite directions so the bond dipoles cancel each other out. Web google classroom in the vapor phase, formic acid exists as dimers (complexes consisting of two formic acid molecules) rather than individual molecules. Intermolecular forces worksheet answers for each of the following compounds, determine the main intermolecular force. What holds molecules of water together? Therefore, stronger intermolecular forces result in higher. How are boiling points affected by intermolecular forces? Explain the difference between a chemical bond and an intermolecular force. Web in this activity worksheet, students will examine the intermolecular forces between covalent molecules including: Include in your explanation how they work on the submicroscopic level. The forces that hold molecules together in the liquid and solid states are called intermolecular forces and are appreciably weaker. Which of the following diagrams correctly represents the hydrogen bonding (denoted by dotted lines) in the formic acid dimer? Choose an answer and hit. Define surface tension and viscosity. Valence electrons form mobile sea of electrons which comprise the metallic bond. Which of these has only london forces? _types of solids intermolecular force(s) between particles_* 1. 1) nitrogen van der waals/london dispersion What hold the o and h atoms together in a molecule of water? We will concentrate on the forces between molecules in molecular substances, which are called intermolecular forces. Define surface tension and viscosity. What hold the o and h atoms together in a molecule of water? Rank the lattice energy (ionic bond strength) for the following formulas, 1 being strongest: Even though the bonds are polar they point in opposite directions so the bond dipoles cancel each other out. Chemical bonds (e.g., covalent bonding) are intramolecular forces which hold atoms together as molecules. Coulomb’s law states that the interaction between two charged particles is stronger the larger the charges and the closer they are together. What holds molecules of fluorine together? Which of the following diagrams correctly represents the hydrogen bonding (denoted by dotted lines) in the formic acid dimer? Explain the difference between a chemical bond and an intermolecular force. Web intermolecular forces, ionic bond strength, phase diagrams, heating curves. Equal sharing of electrons within the covalent bonds of a molecule results in a _____ molecule. Which force must be strongest in order for an ionic substance to dissolve? Tell what type of intermolecular force is important in converting each of the following from a gas to a liquid (a) co2; Web chapter 10 practice worksheet: What holds nacl(aq) together in salt water? Include in your explanation how they work on the submicroscopic level.Intermolecular Forces PRACTICE Test
Worksheet 15 Intermolecular Forces Chemical bonds are
115 Intermolecular Force Worksheet Key (1) Chemical Polarity
w317 Intermolecular Forces Worksheet
Intermolecular Forces Worksheet Forces Worksheet Answers are on page 3
Intermolecular Forces Worksheet
Intermolecular Forces Worksheet
Intermolecular Forces Lab Worksheet Answers Download Latest Activation
Intermolecular forces worksheet
Intermolecular Forces Worksheet Pdf Answer Key Kidsworksheetfun
Therefore, Stronger Intermolecular Forces Result In Higher.
Compare The Relative Amounts Of Energy Involved In The Forming And Breaking Of These Forces.
Answer The Following Questions With “Increase,” “Not Change,” Or “Decrease.” A.
Al 2S 3 Mgo Mgcl 2 Nacl Strategy:
Related Post: