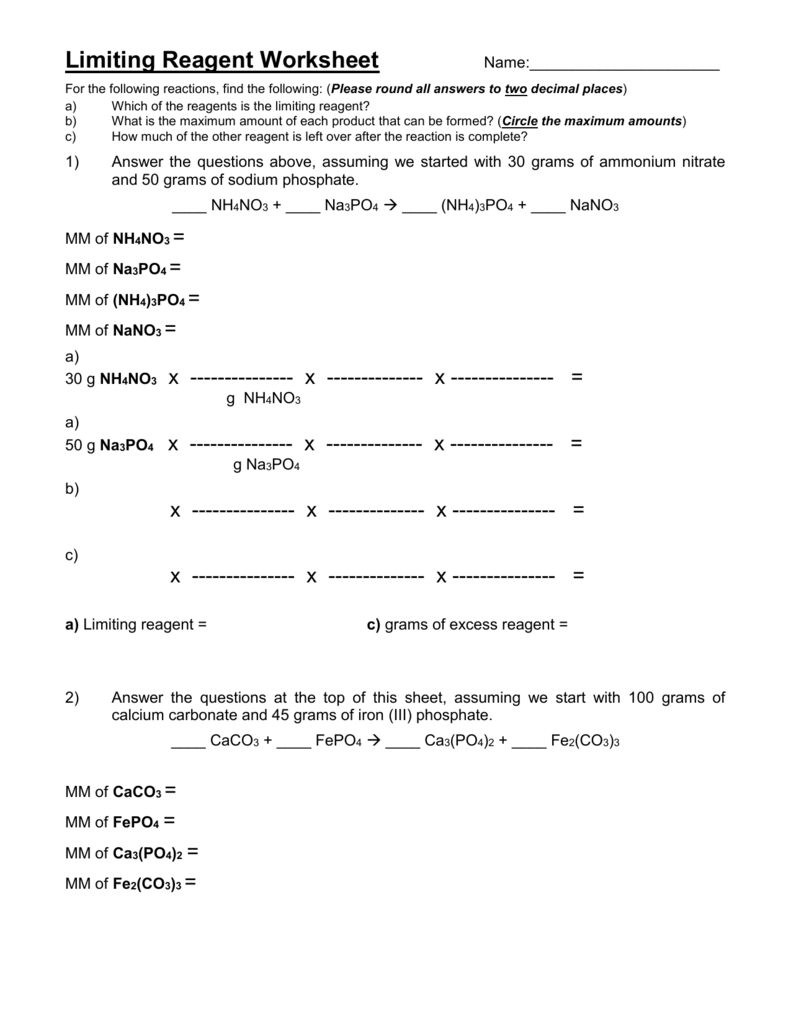
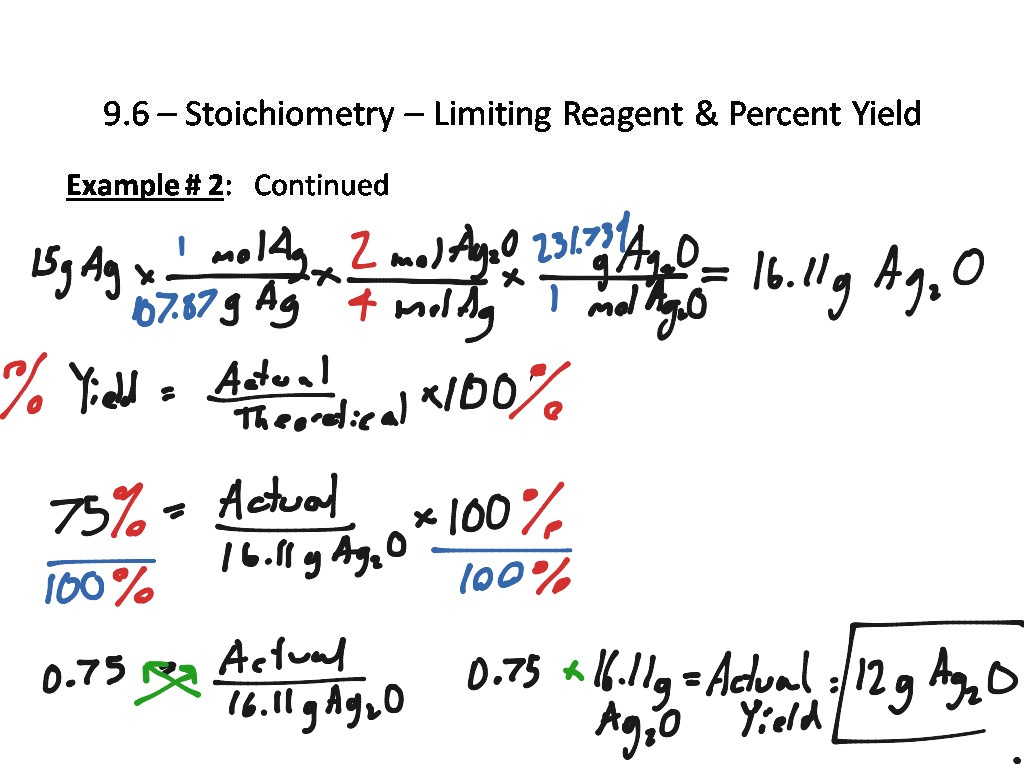
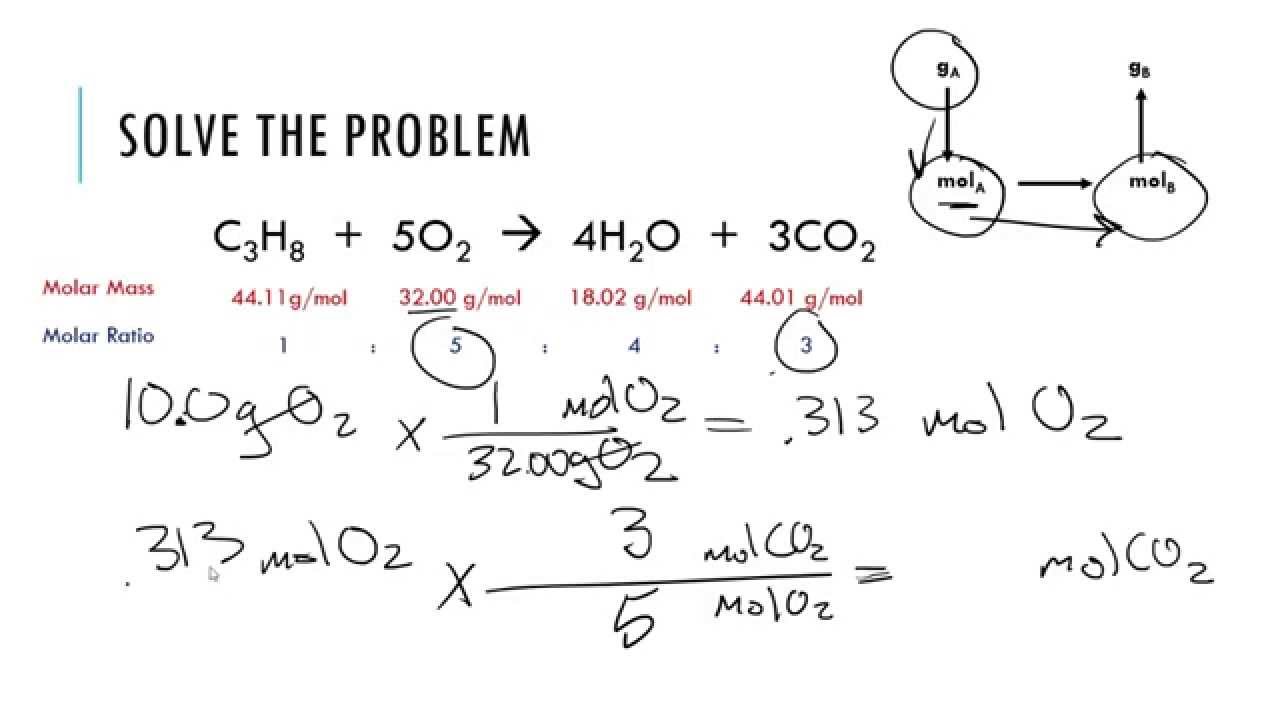
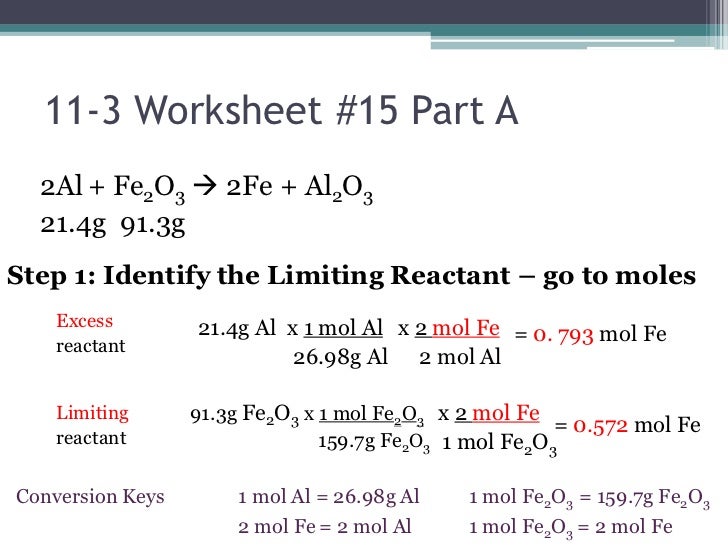
Limiting Reagent Stoichiometry Worksheet
Limiting Reagent Stoichiometry Worksheet - If 4.7 g of nitrogen reacts with. 5 questions practice what you’ve learned, and level up on the above skills. Web understand the concept of the limiting reagent success criteria convert between numbers of atoms, moles, and mass of sample by using avogadro’s number. Pb (no3)2 (aq) + 2 nai. 10.0 g / 342.2948 g/mol = 0.0292146 mol 2) calculate moles of oxygen required to react with. Web identifying the limiting and excess reactants for a given situation requires computing the molar amounts of each reactant provided and comparing them to the. Identify moles of all reactants present. Web which is the limiting reagent? 15 how much of the excess reagent. Web this worksheet allows students to practice using stoichiometry to solve limiting reagent problems. 15 how much of the excess reagent. .show all work (including balanced equations). If 4.7 g of nitrogen reacts with. (unbalanced) al 2 (so 3) 3 + naoh na 2 so 3 + al(oh) 3 5) if 10.0 g of al 2 (so 3) 3 is. Web understand the concept of the limiting reagent success criteria convert between numbers of. .show all work (including balanced equations). Students will need a good understanding of stoichiometry and limiting. Students will need a good understanding of stoichiometry and limiting. Web and the reagent that leads to this answer is the limiting reagent. 14) what is the limiting reagent in problem #2? Web this worksheet allows students to practice using stoichiometry to solve limiting reagent problems. Web what is the limiting reagent? 2c2h2(g) + 5o2(g) → 4co2(g) + 2h2o(l) 3. Web identifying the limiting and excess reactants for a given situation requires computing the molar amounts of each reactant provided and comparing them to the. 10.0 g / 342.2948 g/mol = 0.0292146. Web and the reagent that leads to this answer is the limiting reagent. 10.0 g / 342.2948 g/mol = 0.0292146 mol 2) calculate moles of oxygen required to react with. (unbalanced) al 2 (so 3) 3 + naoh na 2 so 3 + al(oh) 3 5) if 10.0 g of al 2 (so 3) 3 is. Nitrogen gas can react. If 4.7 g of nitrogen reacts with. 2c2h2(g) + 5o2(g) → 4co2(g) + 2h2o(l) 3. (unbalanced) al 2 (so 3) 3 + naoh na 2 so 3 + al(oh) 3 5) if 10.0 g of al 2 (so 3) 3 is. Web identifying the limiting and excess reactants for a given situation requires computing the molar amounts of each reactant. 10.0 g / 342.2948 g/mol = 0.0292146 mol 2) calculate moles of oxygen required to react with. Web up to 24% cash back stoichiometry/limiting reagent practice ap chemistry (practice, practice, practice. 15 how much of the excess reagent. Students will need a good understanding of stoichiometry and limiting. 2 nh3 (g) + 3 cuo (s) n2 (g) + 3 cu. Students will need a good understanding of stoichiometry and limiting. Web what is the limiting reagent? (unbalanced) al 2 (so 3) 3 + naoh na 2 so 3 + al(oh) 3 5) if 10.0 g of al 2 (so 3) 3 is. Web understand the concept of the limiting reagent success criteria convert between numbers of atoms, moles, and mass. Nitrogen gas can react with hydrogen gas to form gaseous ammonia. Web this worksheet allows students to practice using stoichiometry to solve limiting reagent problems. 2 nh3 (g) + 3 cuo (s) n2 (g) + 3 cu (s) + 3 h2o (g) ans: 15 how much of the excess reagent. 5 questions practice what you’ve learned, and level up on. Students will need a good understanding of stoichiometry and limiting. If 4.7 g of nitrogen reacts with. 10.0 g / 342.2948 g/mol = 0.0292146 mol 2) calculate moles of oxygen required to react with. Web identifying the limiting and excess reactants for a given situation requires computing the molar amounts of each reactant provided and comparing them to the. Identify. 2 nh3 (g) + 3 cuo (s) n2 (g) + 3 cu (s) + 3 h2o (g) ans: 5 questions practice what you’ve learned, and level up on the above skills. Students will need a good understanding of stoichiometry and limiting. 15 how much of the excess reagent. Web and the reagent that leads to this answer is the limiting. (from a complete oli stoichiometry course) we are now ready to pull everything we know about reaction stoichiometry together,. If given mass, divide by formula weight to convert to moles (this is the mass to mole step from the. 1) calculate moles of sucrose: Web this worksheet allows students to practice using stoichiometry to solve limiting reagent problems. 15 how much of the excess reagent. Pb (no3)2 (aq) + 2 nai. If 4.7 g of nitrogen reacts with. Identify moles of all reactants present. 14) what is the limiting reagent in problem #2? It will be based on the mass of the reactants present, and on the stoichiometry of the reaction. Web identifying the limiting and excess reactants for a given situation requires computing the molar amounts of each reactant provided and comparing them to the. 10.0 g / 342.2948 g/mol = 0.0292146 mol 2) calculate moles of oxygen required to react with. When 50.0 g of mgco3 react completely with h3po4, as shown below,15.8 g of co2 is produced. Web which is the limiting reagent? Students will need a good understanding of stoichiometry and limiting. Web given the equation below, determine the limiting reactant, and calculate how many grams of cu can be formed from the reaction of 18.1 g of nh3 and 90.4 g of cuo. Web this worksheet allows students to practice using stoichiometry to solve limiting reagent problems. 5 questions practice what you’ve learned, and level up on the above skills. (unbalanced) al 2 (so 3) 3 + naoh na 2 so 3 + al(oh) 3 5) if 10.0 g of al 2 (so 3) 3 is. Web the principles of stoichiometry and limiting reagents will be used to predict the amount of product that should be produced when mixing two solutions to produce an insoluble. Students will need a good understanding of stoichiometry and limiting. 5 questions practice what you’ve learned, and level up on the above skills. 1) calculate moles of sucrose: 15 how much of the excess reagent. Web the principles of stoichiometry and limiting reagents will be used to predict the amount of product that should be produced when mixing two solutions to produce an insoluble. (from a complete oli stoichiometry course) we are now ready to pull everything we know about reaction stoichiometry together,. .show all work (including balanced equations). If given mass, divide by formula weight to convert to moles (this is the mass to mole step from the. It will be based on the mass of the reactants present, and on the stoichiometry of the reaction. Web this worksheet allows students to practice using stoichiometry to solve limiting reagent problems. When 50.0 g of mgco3 react completely with h3po4, as shown below,15.8 g of co2 is produced. Web what is the limiting reagent? Web given the equation below, determine the limiting reactant, and calculate how many grams of cu can be formed from the reaction of 18.1 g of nh3 and 90.4 g of cuo. 2 nh3 (g) + 3 cuo (s) n2 (g) + 3 cu (s) + 3 h2o (g) ans: Web understand the concept of the limiting reagent success criteria convert between numbers of atoms, moles, and mass of sample by using avogadro’s number. 2c2h2(g) + 5o2(g) → 4co2(g) + 2h2o(l) 3.Limiting Reagent Worksheet
Stoichiometry Limiting Reagent Worksheet Photos Cantik
Stoichiometry Worksheet 6 Limiting Reactant Learning Target
Limiting Reagent And Percent Yield Worksheet Worksheet List
stoichiometry worksheet limiting reagent
Limiting Reagent Worksheet 2
Stoichiometry Limiting Reagent Worksheet Instructional Fair canvas
Limiting Reagent Worksheet Answer Key Kayra Excel
Stoichiometry Limiting Reagent Worksheet Answers —
Stoichiometry, Percent Yield and Limiting Reagents practice problems
Web Identifying The Limiting And Excess Reactants For A Given Situation Requires Computing The Molar Amounts Of Each Reactant Provided And Comparing Them To The.
Web This Worksheet Allows Students To Practice Using Stoichiometry To Solve Limiting Reagent Problems.
If 4.7 G Of Nitrogen Reacts With.
Web Up To 24% Cash Back Stoichiometry/Limiting Reagent Practice Ap Chemistry (Practice, Practice, Practice.
Related Post: