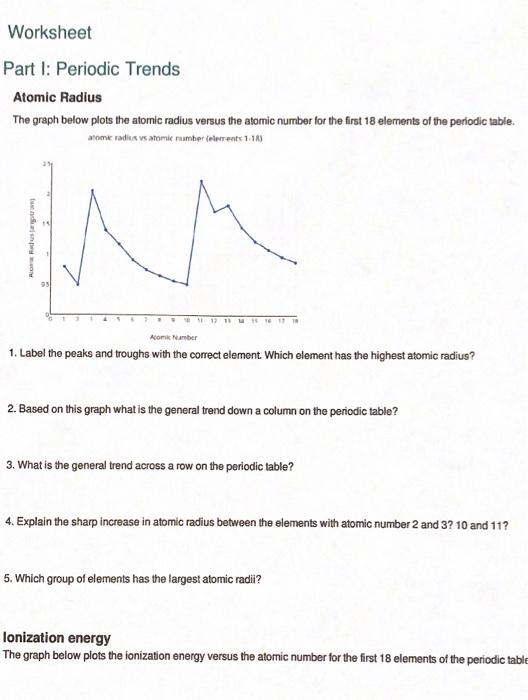
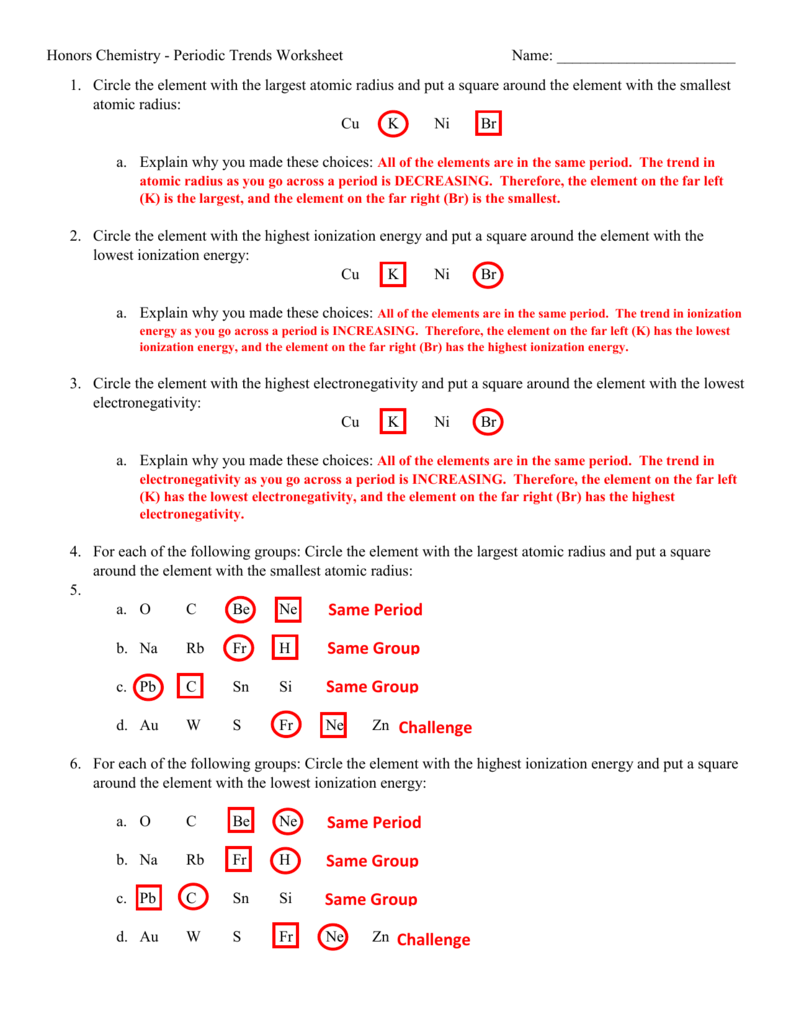
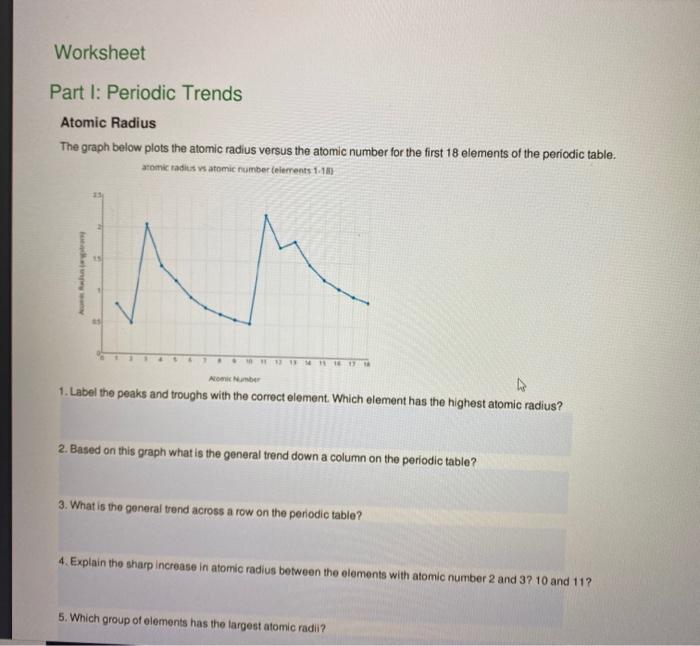
Periodic Trends Atomic Radius Worksheet Answers
Periodic Trends Atomic Radius Worksheet Answers - Web use the periodic table and your knowledge of periodic trends to answer the following questions. Which atom in each pair has the larger atomic radius? Li, c, f li, na, k ge, p, o c, n, al al, cl, ga ionic radius for each of the following sets of ions, rank them from smallest to largest ionic radius. Web periodic trends answer key vocabulary:atomic radius, electron affinity, electron cloud, energy level, group, ion, ionization energy, metal, nonmetal, nucleus, period, periodic trends, picometer, valence electron prior knowledge questions(do these before using the gizmo.) students are not expected to know the answer to the prior knowledge. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like rank the following elements by increasing atomic radius: Increase due to shielding of outer electrons by inner electrons. Carbon, aluminum, oxygen, potassium, rank the following elements by increasing electronegativity: Web major periodic trends include: Predict differences in ionic radius for various oxidation states of the same element. Describe specific reasons for this variation across a period and within a group. Mg , si b.mg , ca , ba c. Let’s take a closer look at atomic radius. Li, c, f li, na, k ge, p, o c, n, al al, cl, ga ionic radius for each of the following sets of ions, rank them from smallest to largest ionic radius. Label the peaks and troughs with the correct element. Using. The atomic radius gets smaller as atomic number increases. Hence the energy required to do so (ionization energy) increases. Web periodic trend the atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period. What trend in atomic radius do you see as you go across a period/row on the periodic table? A) li or kb) caor ni. Predict differences in atomic radius and ionic radius for the same element; Which atom in each pair has the larger atomic radius? Li, c, f li, na, k ge, p, o c, n, al al, cl, ga ionic radius for each of the following sets of ions, rank them from smallest to largest ionic radius. Rank the following elements by. The atomic radius gets larger as atomic number increases. Which atom in each pair has the larger atomic radius? This explains why argon (z = 18) has a smaller radius than sodium (z = 11). Estimate the size of the largest. 1.) describe what a periodic table is. 1 p 0 answer the following questions. So it becomes harder to remove electron from the atom. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like rank the following elements by increasing atomic radius: Rank the following elements by increasing electronegativity: The bonding atomic radius of an element is taken as one half the distance between the nuclei when. Rank the following elements by increasing electronegativity: Web atomic radius for each of the following sets of atoms, rank the atoms from smallest to largest atomic radius. A periodic table is a tabular arrangement of chemical elements. A) li or k b) ca or ni c) ga or b d) o or c e) cl or br Al or b. Increase due to shielding of outer electrons by inner electrons. Web use the periodic table and your knowledge of periodic trends to answer the following questions. Web side of the periodic table have more protons though. The atomic size becomes smaller from left to right. Explain why this trend occurs. Periodic trends atomic radius the graph below plots the atomic radius versus the atomic number for the first 18 elements of the periodic table. Web periodic trends answer key vocabulary:atomic radius, electron affinity, electron cloud, energy level, group, ion, ionization energy, metal, nonmetal, nucleus, period, periodic trends, picometer, valence electron prior knowledge questions(do these before using the gizmo.) students are. Web periodic trend the atomic radius of atoms generally decreases from left to right across a period. A) li or k b) ca or ni c) ga or b d) o or c e) cl or br Web ionization energy increases from left to right across the period. 1.) describe what a periodic table is. Study the figures below and. Electronegativity, ionization energy, electron affinity, atomic radius, melting point, and metallic character. Circle the atom in each pair that has the largest atomic radius. Web atomic radius for each of the following sets of atoms, rank the atoms from smallest to largest atomic radius. The atomic radius gets larger as atomic number increases. Li, c, f li, na, k ge,. Rank the following elements by increasing atomic radius: Web make a prediction about the following trends you expect to see in atomic radius: This explains why argon (z = 18) has a smaller radius than sodium (z = 11). A) li or k b) ca or ni c) ga or b d) o or c e) cl or br Circle the atom in each pair that has the largest atomic radius. Describe specific reasons for this variation across a period and within a group. Predict differences in ionic radius for various oxidation states of the same element. The atomic radius gets smaller as atomic number increases. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like rank the following elements by increasing atomic radius: Within a period, protons are added to the nucleus as electrons are being added to the same principal energy level. The atomic radius decreases across a period from left to right. Al, cl, ga cli ionic radius for each of the following sets of ions, rank them from smallest to largest ionic radius. As you move down a group? Web the atomic radius increases down the group in the elements of the same group. Web atomic radius for each of the following sets of atoms, rank the atoms from smallest to largest atomic radius. Rank the following elements by increasing electronegativity: We will consider theoretical values determined from quantum mechanical wave functions. 1.) describe what a periodic table is. What trend in atomic radius do you see as you go across a period/row on the periodic table? Hence the energy required to do so (ionization energy) increases. Circle the atom in each pair that has the largest atomic radius. As you move across a period? The atomic radius gets smaller as atomic number increases. Mg , si b.mg , ca , ba c. Hence the energy required to do so (ionization energy) increases. Periodic trends worksheet name_____score:_____/ 56 use the periodic table and your knowledge of periodic trends to answer the following questions. Web use the periodic table and your knowledge of periodic trends to answer the following questions. Li, c, f li, na, k ge, p, o c, n, al al, cl, ga ionic radius for each of the following sets of ions, rank them from smallest to largest ionic radius. We will consider theoretical values determined from quantum mechanical wave functions. Web predict the variation in atomic radius in the periodic table. Carbon, aluminum, oxygen, potassium, rank the following elements by increasing electronegativity: What trend in atomic radius do you see as you go across a period/row on the periodic table? The atomic radius decreases across a period from left to right. The atomic size becomes smaller from left to right. This results in a larger attraction for the electrons and a smaller radius. Ca, mg, be be < mg < ca ga, br, ge br < ge < ga al, tl, si si < al < tl zn, cd, fe fe < zn < cd radius of i.Solved Worksheet Part I Periodic Trends Atomic Radius The
Periodic Trends Worksheet 1 answers
Atomic Radius Worksheet
Periodic Trends Worksheet Answers Atomic Radius Worksheet Fun
Periodic Trends Worksheet Atomic Radius Answers Ivuyteq
Gizmo Periodic Trends Answer Key Periodic Trends Atomic Radius
atomic radius worksheet
Atomic Radii Worksheet Atomic Radius Exploration Part Of The
Name ___Date Worksheet Periodic Trends 1. ATOMIC RADIUS
Trends In The Periodic Table Graphing Worksheet Answers
Web Study With Quizlet And Memorize Flashcards Containing Terms Like Rank The Following Elements By Increasing Atomic Radius:
Sulfur, Oxygen, Neon, Aluminum, Why Does Fluorine Have A Higher Ionization Energy Than Iodine?
This Explains Why Argon (Z = 18) Has A Smaller Radius Than Sodium (Z = 11).
Atomic Radius For Each Of The Following Sets Of Atoms, Rank The Atoms From Smallest To Largest Atomic Radius.
Related Post: