Sea Star Dissection Worksheet
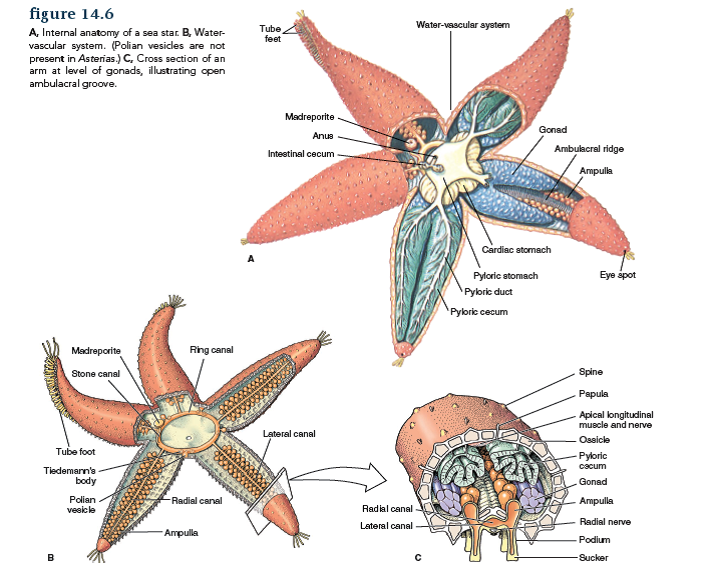
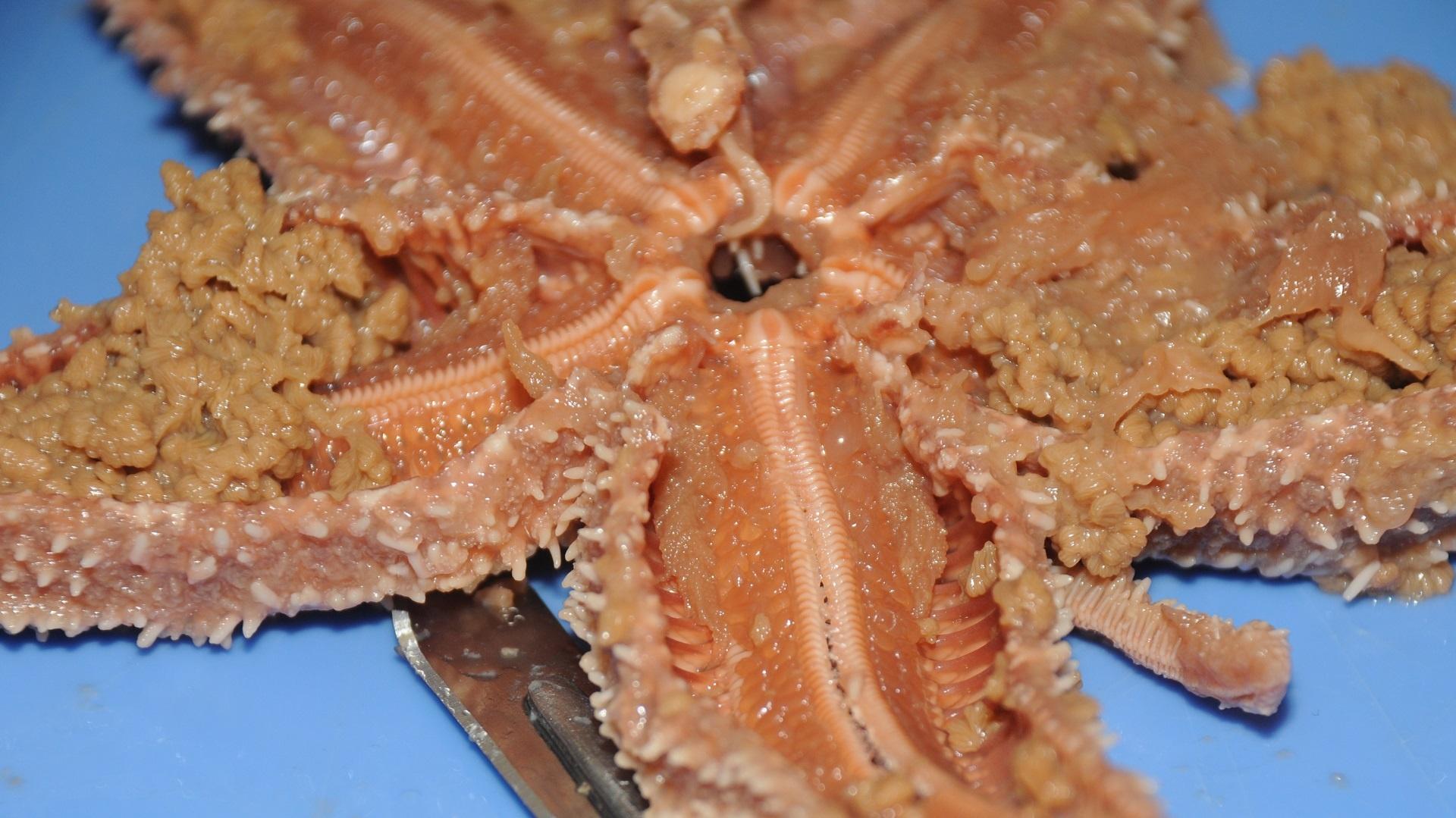
Sea Star Dissection Worksheet - List and describe the three types of symmetry. Web in this simple dissection of a starfish, you’ll learn various parts of the echinoderm anatomy, how starfish eat, and why starfish shouldn’t be called starfish. Which side is the aboral side? The lesson includes educational videos, an interactive quiz, a student checklist, an interactive laboratory powerpoint, and more! Place the starfish in the dissecting pan with its dorsal or aboral (top) surface upward. A pair of arms, the bivium, borders the madreporite. Many, but not all, echinoderms have spiny skin. This can be done prior to class. Web sea star dissection click on one of the video options below to view the sea star dissection. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like echinodermata, sea, ocean, clams mussels oysters and more. Muscles within the feet are used to retract them. Draw an organism that represents each type and draw a line or lines to show how the symmetry occurs. Web by moving water from the vascular system into the tiny feet, the sea star can make a foot move by expanding it. Echinoderms mean “spiny skin” in greek. Locate the central. Draw the shape of the scales. Sets found in the same folder. If the function is not addressed in either of these resources, you may use google searches. Web what kind of skeletal structure do sea stars have? Locate the central disk and the aboral madreporite. E chinoderms are radially symmetrical animals that are only found in the sea (there are none on land or in fresh water). Star sea stars (starfish) are echinoderms, which are an unusual group of marine. Worksheets are starfish pre lab work, starfish dissection guide, starfish dissection lab biology junction answer key, crayfish dissection, starfish dissection guide, skills practice lab analyzing. Many, but not all, echinoderms have spiny skin. Web what kind of skeletal structure do sea stars have? Use lines provided for additional notes external structures orientation o top view, also called the aboral (opposite mouth) surface. ¨ arms or rays : List and describe the three types of symmetry. Cs 3305 unit 8 learning journal.docx. External anatomy 1.look at the fish's skin, including under the dissecting scope. Place the starfish on your dissection tray with its aboral surface facing upward. There are over 2,000 different species of sea stars worldwide. A pair of arms, the bivium, borders the madreporite. Web by moving water from the vascular system into the tiny feet, the sea star can make a foot move by expanding it. Using your diagram sheets and the pictures below to locate the following structures, and note their functions: Web fish dissection examine and sketch the external and internal anatomy: A pair of arms, the bivium, borders the madreporite.. A pair of arms, the bivium, borders the madreporite. Web sea star dissection lab i. Purpose the purpose of this lab is to observe the structure and. Locate the central disc in the center of the starfish. Using your diagram sheets and the pictures below to locate the following structures, and note their functions: Sea stars move very slowly along the sea bed, using hundreds of tiny tube feet. External anatomy 1.look at the fish's skin, including under the dissecting scope. Web in this video, host steven rokusek and professor dale droge dissect a sea star and explain its external anatomy. A pair of arms, the bivium, borders the madreporite. Worksheets are starfish pre. Web there are three main types of symmetry. Distinguish the oral side from the aboral side. Web biology two dissection the starfish phylum echinodermata class asteroidea. Even though sea stars are. Web sea star dissection click on one of the video options below to view the sea star dissection. Part ii (internal anatomy), additional video, lesson plans, quizzes, additional dissections, and more available in support materials and. External anatomy 1.look at the fish's skin, including under the dissecting scope. These are the five extensions that you see projecting from the middle of the starfish. Watch the dissection video and fill out this function table as you go. Worksheets are. Echinoderms are radially symmetrical animals that are only found in the sea. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like echinodermata, sea, ocean, clams mussels oysters and more. Using your diagram sheets and the pictures below to locate the following structures, and note their functions: Sea stars (starfish) are echinoderms, which are an unusual group of marine animals. Draw an organism that represents each type and draw a line or lines to show how the symmetry occurs. List and describe the three types of symmetry. Pdf version interactive dissection powerpoint: If the function is not addressed in either of these resources, you may use google searches. Web this lesson plan describes the sea star (starfish) dissection in detail. Each ray of a sea star has a light sensitive organ called an eyespot. Star sea stars (starfish) are echinoderms, which are an unusual group of marine. Sea star have radial symmetry. Anterior dorsal, posterior dorsal, caudal (tail), anal, pelvic, and pectoral fins. External anatomy 1.look at the fish's skin, including under the dissecting scope. Web in this video, host steven rokusek and professor dale droge dissect a sea star and explain its external anatomy. Locate the central disk and the aboral madreporite. E chinoderms are radially symmetrical animals that are only found in the sea (there are none on land or in fresh water). Draw the shape of the scales. Obtain a preserved starfish and rinse off any preservative with water. Web what kind of skeletal structure do sea stars have? Locate the central disc in the center of the starfish. Distinguish the oral side from the aboral side. Place the starfish on your dissection tray with its aboral surface facing upward. Determine the range of motion possible for each fin. A lesson plan (with time codes), quiz and an interactive powerpoint are available below. List and describe the three types of symmetry. Place the starfish in the dissecting pan with its dorsal or aboral (top) surface upward. E chinoderms are radially symmetrical animals that are only found in the sea (there are none on land or in fresh water). Web biology two dissection the starfish phylum echinodermata class asteroidea. Each ray of a sea star has a light sensitive organ called an eyespot. The other arms form the trivium. There are over 6,000 species. Sea stars move very slowly along the sea bed, using hundreds of tiny tube feet. Use lines provided for additional notes external structures orientation o top view, also called the aboral (opposite mouth) surface. Pdf version interactive dissection powerpoint: Web this lesson plan describes the sea star (starfish) dissection in detail.Marine Biology Lab Sea Star Dissection
starfish dissection
Starfish Dissection Guide
32 Starfish Label The Parts Labels Design Ideas 2020
starfish anatomy Google Search Starfish, Brittle star
Pin on Life science
Starfish Dissection
Dissection 101 Sea Star Dissection Lesson Plan PBS LearningMedia
Echinodermata Biology 11
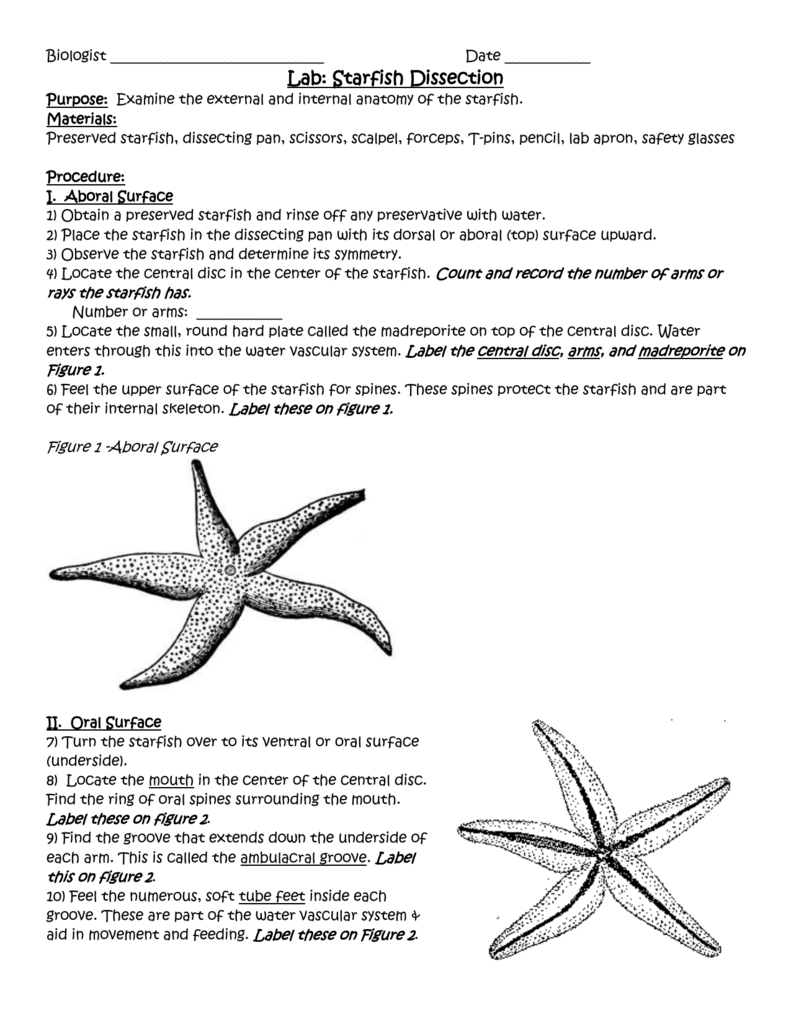
Lab Starfish Dissection
Purpose The Purpose Of This Lab Is To Observe The Structure And.
Part Ii (Internal Anatomy), Additional Video, Lesson Plans, Quizzes, Additional Dissections, And More Available In Support Materials And.
Seastar Dissection Protocol Introduction :
Echinoderms Are Radially Symmetrical Animals That Are Only Found In The Sea.
Related Post: