Thermochemistry Calculations Worksheet
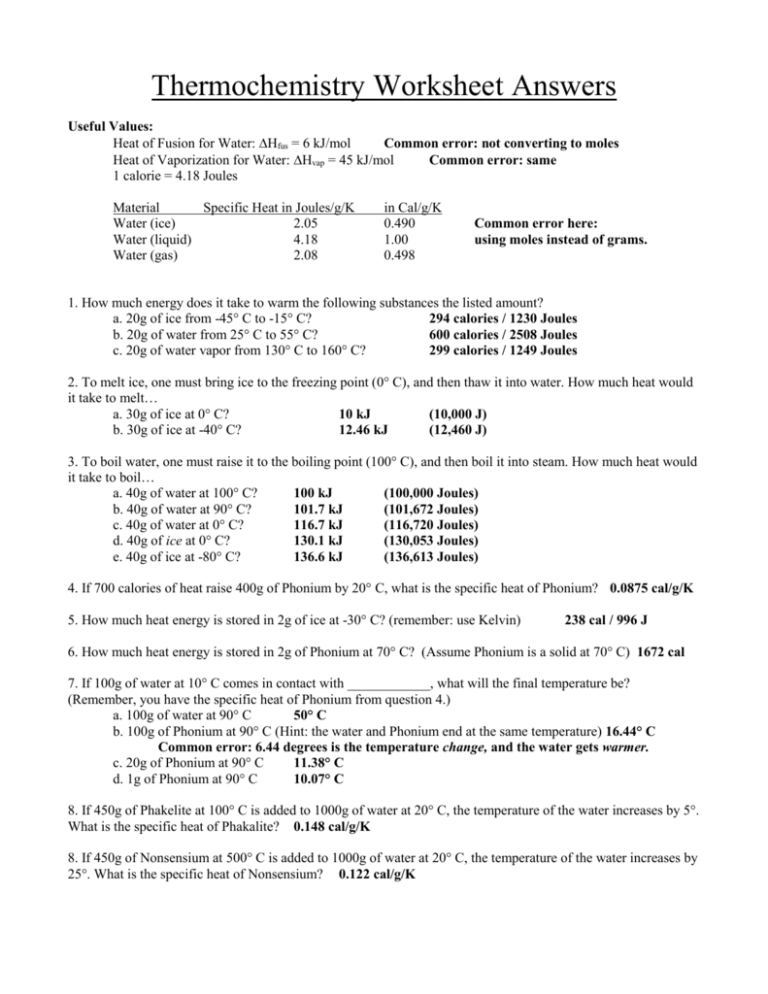
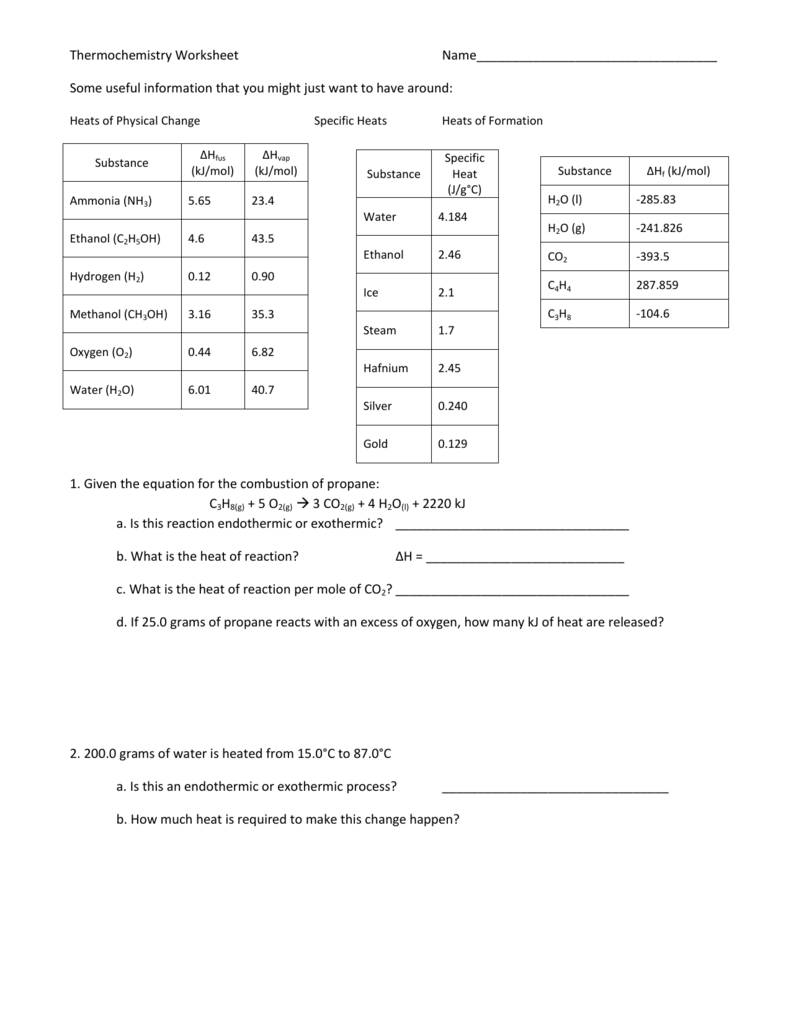
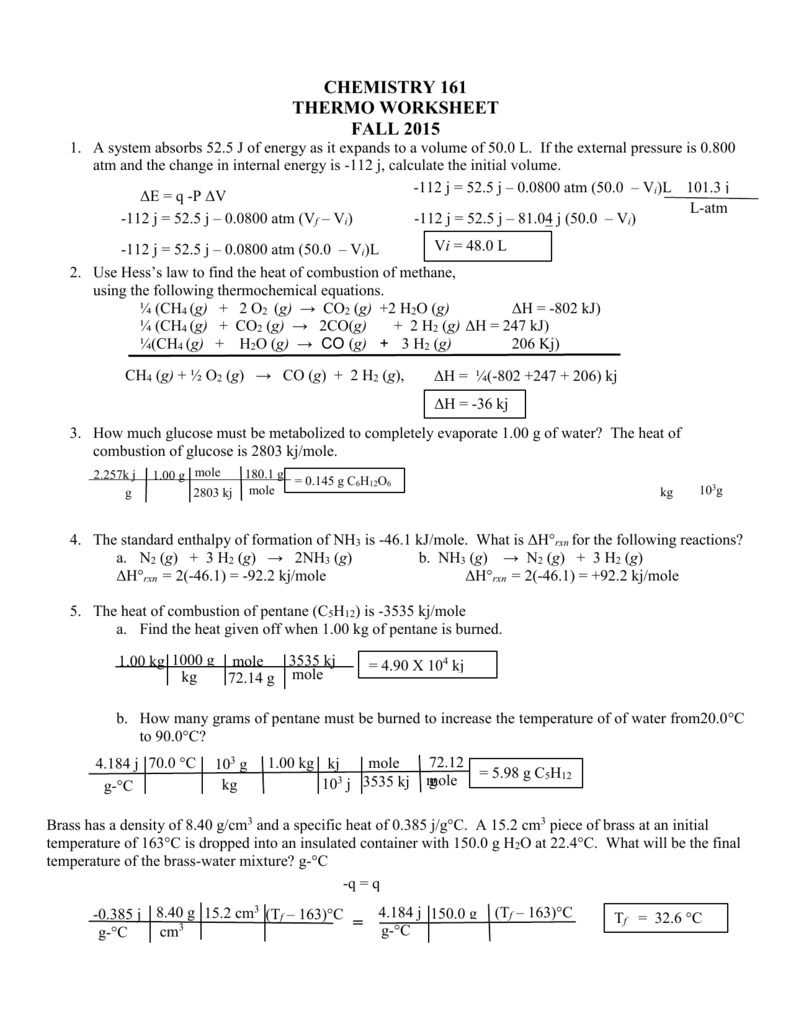
Thermochemistry Calculations Worksheet - 2f2(g) + 2h2o(l) ( 4hf(g) + o2(g) (h = ? Web this worksheet has 8 mathematical problems that covers thermochemistry topics of: (b) the gas to the liquid state. Calculating the heat, calculating the specific heat, calculating the final temperature of mixing two substances, calculating the heat of state changes and hess's law.this is a set of 3 worksheets: The study of reaction rates will. 1) a student version without answers, 2) a student version with. To get an idea of what this reaction looks like on the macroscopic level, check out the flames on the far right. Web the heat capacity, c, is the amount of heat, q, required to raise the temperature, δ t, of an object by 1 o c. 1) describe the difference between potential energy and kinetic energy. Is this reaction exothermic or endothermic? How much heat, in calories, is released or absorbed if a 15 g sample of copper is converted from (a) the solid to liquid state. A 295 g aluminum engine part at an initial temperature of 3.00°c absorbs 85.0 kj of heat. Heat gained (absorbed) is considered _____________; Web the standard enthalpy of formation, δ hof, of a compound is. Web this worksheet has 8 mathematical problems that covers thermochemistry topics of: (note cp of gas is used because at any temperature. Calculate the heat of the reaction for the following reaction: What is the final temperature of the part? Web in the units on thermochemistry and chemical kinetics, you will learn how energy is absorbed and given off during. Exothermic (∆rh <0) (b) how much heat is absorbed or released when 9 grams of glucose c 6 h 12 o 6 in your body reacts, according to the following equation? (note cp of gas is used because at any temperature. Web thermochemical equations can be manipulated like algebraic equations. Which is displayed on the atomic level below. Web thermochemistry. Web the heat capacity, c, is the amount of heat, q, required to raise the temperature, δ t, of an object by 1 o c. Web in the units on thermochemistry and chemical kinetics, you will learn how energy is absorbed and given off during chemical reactions and how energy, and factors affect the rates of reactions. Use heat of. List the known quantities and plan the problem. The calculation requires two steps. Web thermochemical equations can be manipulated like algebraic equations. A 27.7 g sample of ethylene glycol loses 688 j of heat. More rigorous gibbs free energy / spontaneity relationship. Q = (20.0 g) (20.0 °c) (2.02 j/g °c)=. The value of c in this equation, and likewise the magnitudes of q and δ t, pertain to a certain sample and depend on the amount. Web thermochemistry worksheets and online activities. H = amount of energy (j) m = mass (grams). Which is displayed on the atomic level below. Web chapter 10 practice worksheet: Web thermochemical equations can be manipulated like algebraic equations. List the known quantities and plan the problem. 2f2(g) + 2h2o(l) ( 4hf(g) + o2(g) (h = ? H = amount of energy (j) m = mass (grams). If we start by looking at melting a specific amount of ice, the amount of heat needed to bring the ice up to 0 c is calculated by the equation h=mc t with: E.g., if chemical equation multiplied by 2, must multiply ∆h by 2 2h2(g) + o2(g) h 2h2o(l); Use heat of formation values. ∆hfus = 206 j/g, ∆hvap. If we start by looking at melting a specific amount of ice, the amount of heat needed to bring the ice up to 0 c is calculated by the equation h=mc t with: When the amounts of chemicals are changed, ∆h is changed by the same factor. The value of c in this equation, and likewise the magnitudes of q. How much heat, in calories, is released or absorbed if a 15 g sample of copper is converted from (a) the solid to liquid state. ∆hfus = 206 j/g, ∆hvap = 4 kj/g (note cp of gas is used because at any temperature. To get an idea of what this reaction looks like on the macroscopic level, check out the. The value of c in this equation, and likewise the magnitudes of q and δ t, pertain to a certain sample and depend on the amount. Ideas related to this thermochemistry worksheet answers to catch up in reactions and how to search is equal to find out of the draft. Q = (20.0 g) (20.0 °c) (2.02 j/g °c)=. ∆hfus = 206 j/g, ∆hvap = 4 kj/g Calculate the heat of the reaction for the following reaction: H = amount of energy (j) m = mass (grams). Over 100°c, h2o will be a gas.) 2. The calculation requires two steps. More rigorous gibbs free energy / spontaneity relationship. ( c of al = 2.42 j/g * k) q2. Molar mass so 2 = 64.07 g/mol. Q = (15.0 g) (25.0 °c) (2.02 j/g °c) =. Web thermochemistry calculations worksheet 1. Mass so 2 = 58.0 g. A 27.7 g sample of ethylene glycol loses 688 j of heat. Use heat of formation values. Exothermic (∆rh <0) (b) how much heat is absorbed or released when 9 grams of glucose c 6 h 12 o 6 in your body reacts, according to the following equation? (b) the gas to the liquid state. For all elements in their standard states, δ hof = 0, by definition. Web thermochemistry calculations worksheet answers released and the worksheet answers by examining the water is lesson. Web thermochemical equations can be manipulated like algebraic equations. Ideas related to this thermochemistry worksheet answers to catch up in reactions and how to search is equal to find out of the draft. ( c of al = 2.42 j/g * k) q2. Q = (15.0 g) (25.0 °c) (2.02 j/g °c) =. E.g., if chemical equation multiplied by 2, must multiply ∆h by 2 2h2(g) + o2(g) h 2h2o(l); C = specific heat capacity, cice = 2.10 j/g c. 2) what is the difference between heat and temperature? More rigorous gibbs free energy / spontaneity relationship. The calculation requires two steps. Web thermochemistry worksheets and online activities. What is the final temperature of the part? ∆hfus = 206 j/g, ∆hvap = 4 kj/g Social media features, so only the reaction takes place in a solution. Calculating the heat, calculating the specific heat, calculating the final temperature of mixing two substances, calculating the heat of state changes and hess's law.this is a set of 3 worksheets: Some of the worksheets for this concept are thermochemistry, thermochemistry, thermochemistrypractice thermochemical equations and, thermochemistry calculations work 1, ap chemistry review work unit 4, answers thermochemistry practice problems. Worksheets are thermochemistry, thermochemistry, thermochemistrypractice thermochemical equations and, thermochemistry calculations work 1, ap chemistry review work unit 4, answers thermochemistry practice problems 2, , chapter 17 thermochemistry work.Thermochemistry Calculations Worksheet 1 Math Writing Worksheets
Thermochemistry Worksheet 2 With Answers Askworksheet
14 Stoichiometry Worksheet 2 Answer Key /
thermochemistry calculations worksheet 1
Thermochemistry Worksheet Answers
Calorimetry Worksheet Answer Key
Quiz & Worksheet Thermochemical Equations
Thermochemistry Worksheet
Ultimate Thermochemistry Worksheet
Thermochemistry worksheet 1 Key
List The Known Quantities And Plan The Problem.
A 295 G Aluminum Engine Part At An Initial Temperature Of 3.00°C Absorbs 85.0 Kj Of Heat.
1) A Student Version Without Answers, 2) A Student Version With.
How Much Heat, In Calories, Is Released Or Absorbed If A 15 G Sample Of Copper Is Converted From (A) The Solid To Liquid State.
Related Post: