V R And I In Parallel Circuits Worksheet Answers
V R And I In Parallel Circuits Worksheet Answers - Web at c = at d = ω 9 v r1 = 1 r2 = 2 ω 3 r3 = 1 ω series or parallel? Web use the sample layout below. Web 1) find vt vt = v1 + v2 = 4v 2) know vt = vbranches 3) find i in each branch: Lesson 6, bulbs & batteries side. Web 4) find total current (i t) going farther 5) finding total resistance (r t) once you know v t and i t, you can find r t by ohm’s law: Web the v r and i in parallel circuits ch 8 1 worksheet answer key is perfect for anyone who wants to learn the basics of vr and i in parallel circuits. There are separate pathways for current, one through. Treat each branch as its own series circuit. What is the voltage across the batteries? ∆v=i•r calculations concept builder challenges learners to conduct an analysis of a simple circuit with one resistor ( apprentice difficulty level) and of a. The master difficulty level is. The current in the branches of the circuit (is the same, adds up). Web 1) find vt vt = v1 + v2 = 4v 2) know vt = vbranches 3) find i in each branch: T = __________________ t = __________________ t = __________________ over r1 =. Web the v r and i in parallel. Web at c = at d = ω 9 v r1 = 1 r2 = 2 ω 3 r3 = 1 ω series or parallel? I1 = 4v/1ω = 4 α 2 v 2 v vt = 4 v 1 ω 2 ω 4a 2a it =. Web remember that in a parallel circuit: Three worksheets requiring students to apply. Web remember that in a parallel circuit: 1.5 v / 3 ohms = 0.5 amperes. 2 r r eq 1 2 2 5 7 eq r r eq r 2 3 2 5 7 eq 14 59 2. ∆v=i•r calculations concept builder challenges learners to conduct an analysis of a simple circuit with one resistor ( apprentice difficulty level) and. 2 r r eq 1 2 2 5 7 eq r r eq r 2 3 2 5 7 eq 14 59 2. T = __________________ t = __________________ t = __________________ over r1 =. Web 4) find total current (i t) going farther 5) finding total resistance (r t) once you know v t and i t, you can. Web use the sample layout below. T = __________________ t = __________________ t = __________________ over r1 =. In a series circuit there is. 2 r r eq 1 2 2 5 7 eq r r eq r 2 3 2 5 7 eq 14 59 2. Three worksheets requiring students to apply the v = ir equation to series. What is the voltage across the batteries? R = 4v/6a = 2/3 ω =. There are separate pathways for current, one through. Treat each branch as its own series circuit. 1.5 v / 3 ohms = 0.5 amperes. Web remember that in a parallel circuit: Web at c = at d = ω 9 v r1 = 1 r2 = 2 ω 3 r3 = 1 ω series or parallel? The current in the branches of the circuit (is the same, adds up). R = 4v/6a = 2/3 ω =. Web use the sample layout below. Web in a parallel circuit, there is more than one loop or pathway so charge flow gets split up or recombined at junction points. Web v i r source 12v 12a 1.0 r 1 12v 6.0a 2.0 r 2 12v 4.0a 3.0 r 3 12v 2.0a 6.0 5. Web 4) find total current (i t) going farther 5) finding total. First you have to know that v = joules/coulomb andi = coulombs/second. Web to complete the table, students must be able to use the ∆v=i•r equation and know that the current is everywhere the same in a simple circuit. Lesson 6, bulbs & batteries side. Treat each branch as its own series circuit. There are separate pathways for current, one. Lesson 6, bulbs & batteries side. Therefore current is not the same at every point in the. The current in the branches of the circuit (is the same, adds up). R = 4v/6a = 2/3 ω =. Three worksheets requiring students to apply the v = ir equation to series and parallel circuit problems. Vt =______ rt =______ it = circuit #1 r1 = ____ v1 = ____ i1 = ____ r1 r2 r3 = r3 v3 = ____ i3 = ____ r2 = ____ v2 = ____ i2 = ____. Two 1.5 v batteries are connected in parallel. ∆v=i•r calculations concept builder challenges learners to conduct an analysis of a simple circuit with one resistor ( apprentice difficulty level) and of a. There are separate pathways for current, one through. Web 4) find total current (i t) going farther 5) finding total resistance (r t) once you know v t and i t, you can find r t by ohm’s law: Web in a parallel circuit having three lamps, each electric device has its own path from one terminal of the battery to the other. The voltage drops across each branch (is the same, adds up to) the total. R = 4v/6a = 2/3 ω =. I = amount of current in the circuit (amps) v = battery voltage (volts) r = resistance (from light bulbs, etc.) in the circuit (ohms) electricity: Web at c = at d = ω 9 v r1 = 1 r2 = 2 ω 3 r3 = 1 ω series or parallel? 1.5 v / 3 ohms = 0.5 amperes. First you have to know that v = joules/coulomb andi = coulombs/second. 2 r r eq 1 2 2 5 7 eq r r eq r 2 3 2 5 7 eq 14 59 2. What is the voltage across the batteries? Determine the total voltage (electric potential) for each of the following circuits below. I1 = 4v/1ω = 4 α 2 v 2 v vt = 4 v 1 ω 2 ω 4a 2a it =. Web v i r source 12v 12a 1.0 r 1 12v 6.0a 2.0 r 2 12v 4.0a 3.0 r 3 12v 2.0a 6.0 5. The current in the branches of the circuit (is the same, adds up). This equation gives us the samewattsas p = w/t. If v = ir, then r = v/i. First you have to know that v = joules/coulomb andi = coulombs/second. Web use the sample layout below. Web remember that in a parallel circuit: There are separate pathways for current, one through. Web the v r and i in parallel circuits ch 8 1 worksheet answer key is perfect for anyone who wants to learn the basics of vr and i in parallel circuits. Web 1) find vt vt = v1 + v2 = 4v 2) know vt = vbranches 3) find i in each branch: Web in a parallel circuit having three lamps, each electric device has its own path from one terminal of the battery to the other. 1.5 v / 3 ohms = 0.5 amperes. The master difficulty level is. Determine the total voltage (electric potential) for each of the following circuits below. Web v i r source 12v 12a 1.0 r 1 12v 6.0a 2.0 r 2 12v 4.0a 3.0 r 3 12v 2.0a 6.0 5. I = v/r fuseselectrical power p = vi power equals the voltage times the current.power (inwatts) voltage (involts) current (inamps)electrical power: Three worksheets requiring students to apply the v = ir equation to series and parallel circuit problems. Web to complete the table, students must be able to use the ∆v=i•r equation and know that the current is everywhere the same in a simple circuit. If v = ir, then r = v/i. 2 r r eq 1 2 2 5 7 eq r r eq r 2 3 2 5 7 eq 14 59 2.Series And Parallel Circuits Worksheet Educational Worksheet
V R And I In Parallel Circuits Worksheet Answer Key Stairs Design Blog
V R And I In Parallel Circuits Answer Key Stairs Design Blog
Series And Parallel Circuits Worksheet
How Series And Parallel Circuit Worksheets Pdf Wiring Diagram
Understanding Current In Parallel Circuits Answer Key
Parallel Circuit Answer Key V R And I In Parallel Circuits Answer Key
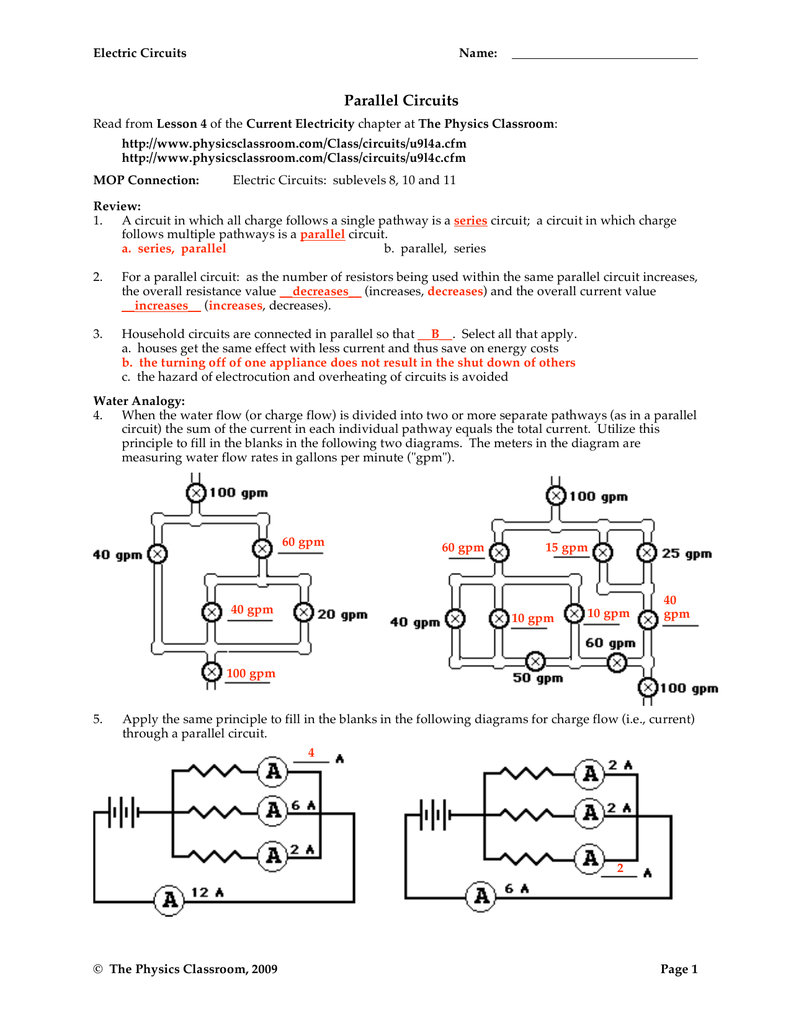
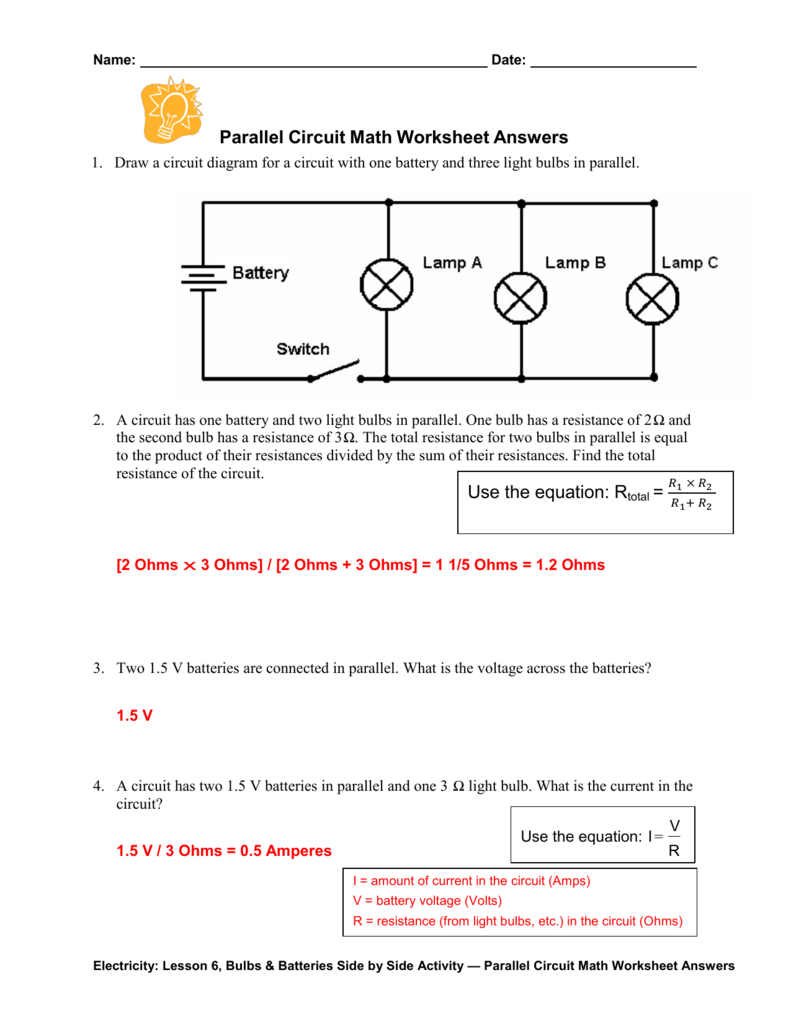
Parallel Circuit Math Worksheet Answers —
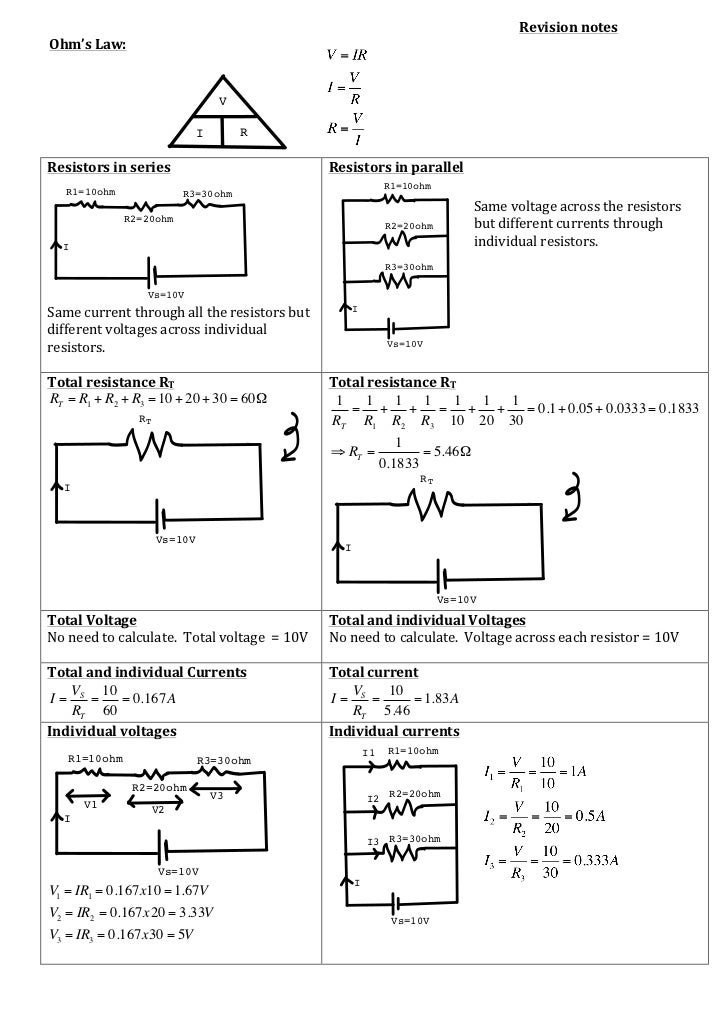
Ohm's law, resistors in series or in parallel
V R And I In Parallel Circuits Worksheet Answers Stairs Design Blog
I1 = 4V/1Ω = 4 Α 2 V 2 V Vt = 4 V 1 Ω 2 Ω 4A 2A It =.
T = __________________ T = __________________ T = __________________ Over R1 =.
R = 4V/6A = 2/3 Ω =.
The Voltage Drops Across Each Branch (Is The Same, Adds Up To) The Total.
Related Post: