Specific Heat Chemistry Worksheet
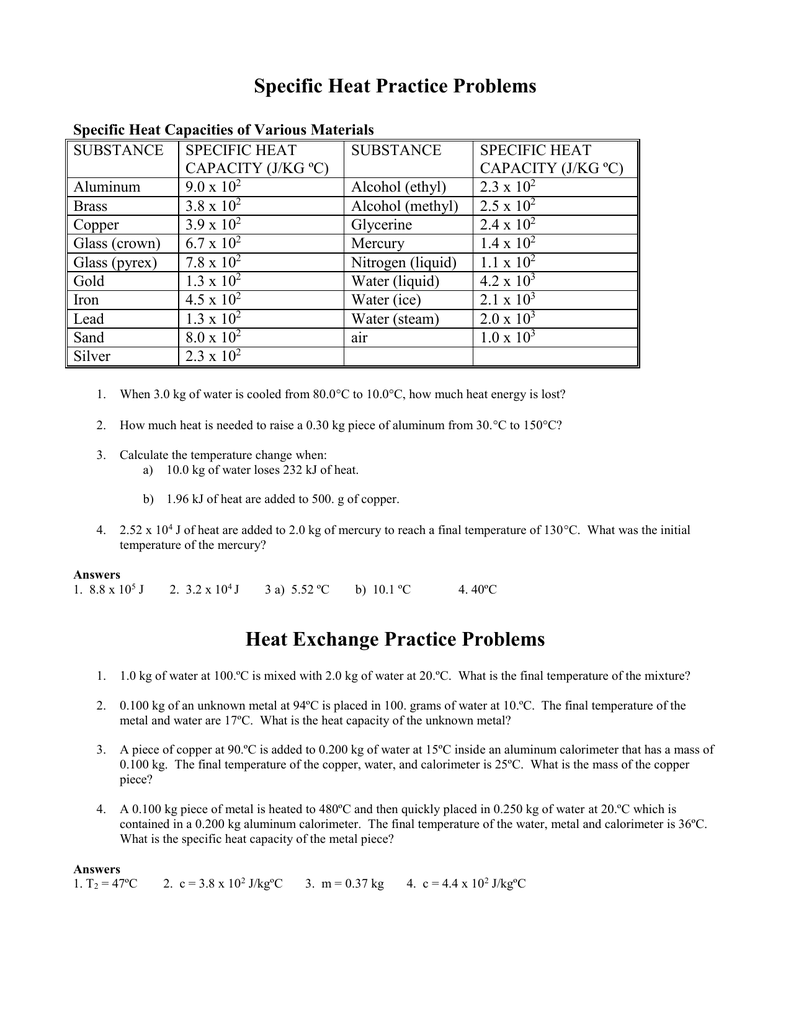
Specific Heat Chemistry Worksheet - •the specific heat capacity (symbol c) of a substance is defined as the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1 oc. Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user. How much heat is lost when a 640 g piece of copper cools from 375oc, to 26oc? A similar question to that in problem 8, and we are going to use the following equation: The equation for ‘quantity of heat’ or enthalpy is: Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron. For q= m c δ t : Use q = (m)(δt)(cp) to solve the following problems. Q = m = c = t = substance specific heat (j/g°c) water (l) 4.184 aluminum (s) 0.897 iron (s) 0.449 mercury (l) 0.140 carbon (s) 0.709 silver (s) 0.24 gold (s) 0.129 copper (s) 0.385 ethanol (l) 2.44 ammonia (g) 2.09 In this worksheet, students will use the specific heat equation (q = mcδt) for a variety of different problems. Determine if it’s endothermic or exothermic. Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron. In this worksheet, students will use the specific heat equation (q = mcδt) for a variety of different problems. Concepts:students will practice calculating heat (q) using the equation q = mc∆t. Calculate the specific heat of iridium. In this worksheet, students will calculate specific heat, energy in joules, the change in temperature, specific heat, and weight in grams. How much heat is absorbed by a 600 g iron cornbread pan when its temperature rises from 22°c Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron. How much heat is needed to convert 550. Q = m tcp] use this. Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron. The temperature of the water rises from 20.1 ºc to 22.6 ºc. Specific heat calculations , comparing specific heats of materials, interpreting heating and cooling graphs of materials, making predictions, calculating rate of change, constructing heating and cooling graphs of materials. Web q = heat absorbed m = mass δt = change in. From these data, what is the specific heat of lead? (remember the specific heat of water is 1 cal/goc). Use q = (m)(δt)(cp) to solve the following problems. The specific heat of iron = 0.450 j/g °c. Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user. A similar question to that in problem 8, and we are going to use the following equation: Use q = (m)(δt)(cp) to solve the following problems. Web dropped from 20°c to 1°c, how much heat did the 150 g can release? Students will solve for heat (joules), mass (g), temperature change (ºc) and specific heat capacity (j. How much heat. A similar question to that in problem 8, and we are going to use the following equation: Students will solve for heat (joules), mass (g), temperature change (ºc) and specific heat capacity (j. •the specific heat capacity (symbol c) of a substance is defined as the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of the substance. Web thermochemistry specific heat calculations. From these data, what is the specific heat of lead? How much heat is needed to raise the temperature of 50.0 g of water by 25.0°c 2. Heat is not the same as temperature, yet they are related. Show all work and proper units. Q = m = c = t = substance specific heat (j/g°c) water (l) 4.184 aluminum (s) 0.897 iron (s) 0.449 mercury (l) 0.140 carbon (s) 0.709 silver (s) 0.24 gold (s) 0.129 copper (s) 0.385 ethanol (l) 2.44 ammonia (g) 2.09 Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron. Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user.. Heat is not the same as temperature, yet they are related. Web specific heat of iridium example problem. Web includes two specific heat worksheets with practice problems for chemistry or physics. For q= m c δ t : The specific heat of iron = 0.450 j/g °c. Heat is not the same as temperature, yet they are related. Calculate the specific heat of iridium. (q= m c δ t) b. Concepts:students will practice calculating heat (q) using the equation q = mc∆t. •heat change gained or lost by a substance during a chemical reaction can be calculated by: Solution to this specific heat chemistry practice problem is given in the video. A similar question to that in problem 8, and we are going to use the following equation: Q = m = c = t = substance specific heat (j/g°c) water (l) 4.184 aluminum (s) 0.897 iron (s) 0.449 mercury (l) 0.140 carbon (s) 0.709 silver (s) 0.24 gold (s) 0.129 copper (s) 0.385 ethanol (l) 2.44 ammonia (g) 2.09 Identify each variables by name & the units associated with it. For q= m c δ t : Web specific heat is a physical property. Science worksheets by john erickson. (q= m c δ t) b. C = t/m ̈t, zheue t = heaw eneug, m = mavv, and t = wempeuawxue remembeu, ̈t =(tfinal ± tinitial). It introduces the concept of specific heat capacity, and includes several problems that require conversions. •heat change gained or lost by a substance during a chemical reaction can be calculated by: In this worksheet, students will use the specific heat equation (q = mcδt) for a variety of different problems. It takes 487.5 j to heat 25 grams of copper from 25 °c to 75 °c. Determine if it’s endothermic or exothermic. Web calculating specific heat extra practice worksheet q = mc∆t, where q = heat energy, m = mass, and ∆t = change in temp. A total of 54.0 joules of heat are absorbed as 58.3 g of lead is heated from 12.0°c to 42.0°c. Students will solve for heat (joules), mass (g), temperature change (ºc) and specific heat capacity (j. Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron. How much heat is lost when a 640 g piece of copper cools from 375oc, to 26oc? Show all work and proper units. How many calories of heat are required to raise the temperature of 550 g of water from 12 to 18? Specific heat table on the back 1. The specific heat capacities of some common substances are shown in the table below. A similar question to that in problem 8, and we are going to use the following equation: An editable word document for this worksheet is included. The specific heat of wood is 2.03 j/g∙°c. How much heat is lost when a 640 g piece of copper cools from 375oc, to 26oc? The specific heat of iron = 0.450 j/g °c. Identify each variables by name & the units associated with it. (q= m c δ t) b. •the specific heat capacity (symbol c) of a substance is defined as the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1 oc. Web calculating specific heat extra practice worksheet q = mc∆t, where q = heat energy, m = mass, and ∆t = change in temp. Specific heats are used to find the quantity of heat, q, that flows into or out of a system. In this worksheet, students will calculate specific heat, energy in joules, the change in temperature, specific heat, and weight in grams. Web specific heat problem. How much heat is needed to convert 550.Calculating Specific Heat Worksheet Worksheets For Home Learning
Specific Heat Worksheet Answers Chemistry Alphabet Worksheets
Specific Heat and Heat Capacity Worksheet
Specific Heat Worksheet PDF Heat Thermodynamic Properties
Other Worksheet Category Page 375
Worksheet Specific Heat + Heat Transfer + Latent Heat
Specific Heat Capacity Worksheet (Key) Specific Heat Capacity L. tL
Honors Chemistry Worksheet Specific Heat
Heat Transfer Specific Heat Problems Worksheet —
specific heat chemistry worksheet
Q = M Tcp] Use This Equation And The Table Of Specific Heats To Solve The Following Problems.
It Introduces The Concept Of Specific Heat Capacity, And Includes Several Problems That Require Conversions.
Web It Introduces The Concept Of Specific Heat Capacity, And Includes Several Problems That Require Conversions.
Use The Formula Q = Mcδt Where Q = Heat Energy M = Mass C = Specific Heat Δt = Change In Temperature Putting The Numbers Into The Equation Yields:
Related Post: