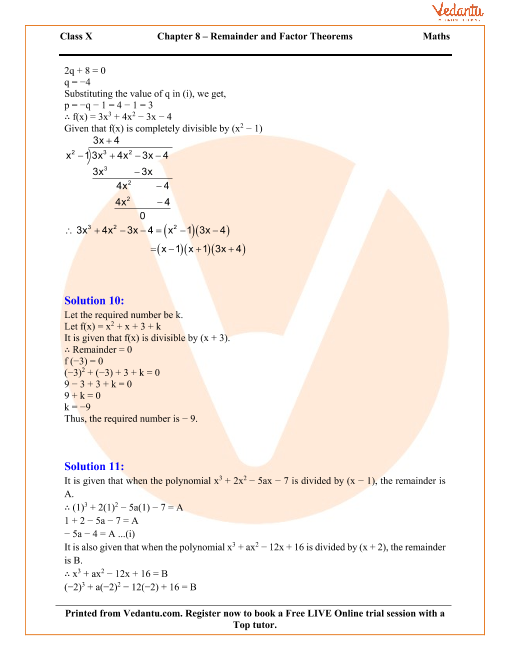
The Remainder And Factor Theorems Worksheet Answers
The Remainder And Factor Theorems Worksheet Answers - Previous fm changing the subject questions. Use long division to find the quotient and the remainder: Jmap archives a/b 2005 ccss: F (x) = x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1. Create your own worksheets like this one with infinite precalculus. Next fm completing the square questions. Find the remainder r by long division and by the remainder theorem. F(x) = x 5 − 2x 4 + 3x 3 − 6x 2 − 4x + 8. Use the remainder theorem to. Jmap on jumbled an online platform for jmap's algebra i resources below: 1) f (x) x x. Free trial available at kutasoftware.com. Here, the divisor is (x + 1). If the remainder when dividing f (x) by x + 2 is 0, what does the remainder theorem tell us? Web use the remainder theorem. Find the remainder r by long division and by the remainder theorem. Is divided by (x + 1). Use the factor theorem to decide if (x − 2) is a factor of. In other words, \[p(x)=d(x)q(x)+r(x)\] because of the division, the remainder will either be zero, or a polynomial of lower degree than d(x). Previous fm changing the subject questions. Web the remainder theorem states the following: Find the remainder obtained when dividing f(x) = 3x3 − 4x2 + x − 2 by (x − 3). When we divide a polynomial, p(x) by some divisor polynomial d(x), we will get a quotient polynomial q(x) and possibly a remainder r(x). Use the remainder theorem to. F (x) = x3 + 3x2. Web 1.10.1 remainder theorem and factor theorem (answers) 1. When we divide a polynomial f (x) by x−c the remainder is f (c) the factor theorem: X + 1 = 0. When we divide a polynomial, p(x) by some divisor polynomial d(x), we will get a quotient polynomial q(x) and possibly a remainder r(x). Web click here for answers. The student must find all possible sets of factors for each polynomial. Find the remainder using the remainder theorem. Find the remainder r by long division and by the remainder theorem. Web remainder theorem and factor theorem worksheets | teaching resources. 7) (k3 − k2 − k − 2) ÷ (k − 2) yes 8) (b4 − 8b3 − b2. Use the remainder theorem to. Polynomial long division algebra index. Web this packet includes the remainder and factor theorem study guide and answer key. Find the remainder when f(x) = x 3 + 3x 2 + 3x + 1 is divided by (x + 1), using the remainder theorem? Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers. Using remainder theorem, find the remainder when. Add to my workbooks (16) embed in my website or blog. Next fm completing the square questions. ( x 4 − 5 x 3 + x 2 − 2 x + 6) ÷ ( x + 4) answer. This self checking worksheet studies factors of polynomials on the front and remainder theorem on. Web click here for answers. 1 2 3 4 5 6. Find the remainder obtained when dividing f(x) = 3x3 − 4x2 + x − 2 by (x − 3). The factor theorem uses the student's knowledge of graphs of polynomial functions and the degree of the polynomial. Equate the divisor to zero. The student must find all possible sets of factors for each polynomial. ( x ) = d ( x ) q ( x ) + r ( x ). Web click here for answers. 7) (k3 − k2 − k − 2) ÷ (k − 2) yes 8) (b4 − 8b3 − b2 + 62 b − 34) ÷ (b. Polynomial long division algebra index. In other words, \[p(x)=d(x)q(x)+r(x)\] because of the division, the remainder will either be zero, or a polynomial of lower degree than d(x). Equate the divisor to zero. If the remainder when dividing f (x) by x + 2 is 0, what does the remainder theorem tell us? When f (c)=0 then x−c is a factor. Web this packet includes the remainder and factor theorem study guide and answer key. Web the factor and remainder theorems. Here, the divisor is (x + 1). Add to my workbooks (16) embed in my website or blog. You will receive your score and answers at the end. X + 1 = 0. Jmap on jumbled an online platform for jmap's algebra i resources below: Because of the division, the remainder will either be zero, or a polynomial of lower degree than d(x). Find the remainder when 2x3+3x2 −17 x −30 is divided by each of the following: When f (c)=0 then x−c is a factor of f (x) when x−c is a factor of f (x) then f (c)=0. Web remainder theorem and factor theorem. In other words, \[p(x)=d(x)q(x)+r(x)\] because of the division, the remainder will either be zero, or a polynomial of lower degree than d(x). Polynomial long division algebra index. 7) (k3 − k2 − k − 2) ÷ (k − 2) yes 8) (b4 − 8b3 − b2 + 62 b − 34) ÷ (b − 7) no 9) (n4 + 9n3 + 14 n2 + 50 n + 9) ÷ (n + 8) no 10) (p4 + 6p3 + 11 p2 + 29 p − 13) ÷ (p + 5) no 11) (p4 − 8p3 + 10 p2 + 2p + 4) ÷ (p − 2) yes 12) (n5 − 25 n3 − 7n2 − 37 n. If the remainder when dividing f (x) by x + 2 is 0, what does the remainder theorem tell us? Choose an answer and hit 'next'. When we divide a polynomial, \(p(x)\) by some divisor polynomial \(d(x)\), we will get a quotient polynomial \(q(x)\) and possibly a remainder \(r(x)\). Web the factor and remainder theorems. Use the factor theorem to decide if (x − 2) is a factor of. The factor theorem uses the student's knowledge of graphs of polynomial functions and the degree of the polynomial. This self checking worksheet studies factors of polynomials on the front and remainder theorem on the back. Web remainder theorem worksheet with answers | remainder theorem questions pdf. Jmap on jumbled an online platform for jmap's algebra i resources below: ( x 4 − 5 x 3 + x 2 − 2 x + 6) ÷ ( x + 4) answer. Add to my workbooks (16) embed in my website or blog. Free trial available at kutasoftware.com. 1 2 3 4 5 6. Web click here for answers. I.e., x + 1 = 0 now. In other words, \[p(x)=d(x)q(x)+r(x)\] because of the division, the remainder will either be zero, or a polynomial of lower degree than d(x). Given that, the function is f(x) = x 3 + 3x 2 + 3x + 1. Web remainder theorem and factor theorem worksheets | teaching resources. Use the remainder theorem to. Use the factor theorem to decide if (x − 2) is a factor of. Web if = 0, then is a factor of. 7) (k3 − k2 − k − 2) ÷ (k − 2) yes 8) (b4 − 8b3 − b2 + 62 b − 34) ÷ (b − 7) no 9) (n4 + 9n3 + 14 n2 + 50 n + 9) ÷ (n + 8) no 10) (p4 + 6p3 + 11 p2 + 29 p − 13) ÷ (p + 5) no 11) (p4 − 8p3 + 10 p2 + 2p + 4) ÷ (p − 2) yes 12) (n5 − 25 n3 − 7n2 − 37 n.42 The Remainder And Factor Theorems Worksheet Answers Worksheet Database
the remainder and factor theorems worksheet
the remainder and factor theorems worksheet answers
The Remainder Theorem Worksheet Answers Ivuyteq
the remainder theorem worksheet for 9th 11th grade lesson
Precalcus The Remainder and Factor Theorem
remainder theorem and factor theorem worksheets teaching remainder
Factor and Remainder Theorems In the classroom Pinterest Math
42 The Remainder And Factor Theorems Worksheet Answers Worksheet Database
the remainder theorem worksheet for 9th 11th grade lesson
Use The Remainder Theorem And Synthetic Division To Find F(K).
Here, The Divisor Is (X + 1).
When We Divide A Polynomial, P(X) By Some Divisor Polynomial D(X), We Will Get A Quotient Polynomial Q(X) And Possibly A Remainder R(X).
Find The Remainder When 2X3+3X2 −17 X −30 Is Divided By Each Of The Following:
Related Post: